1.

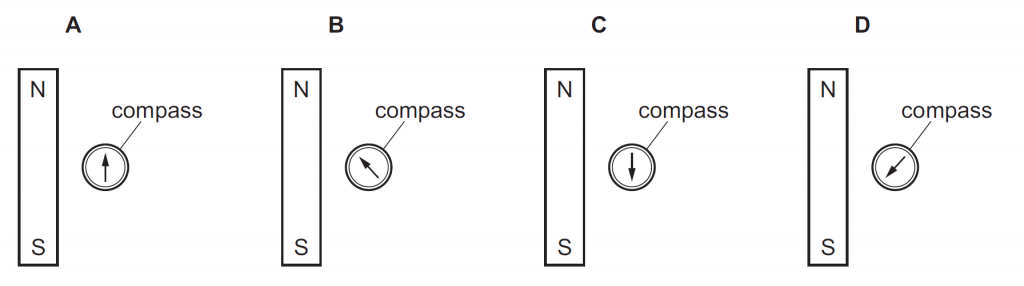
Answer : C
Solution
The compass needle will point in the direction of the magnetic field line, which is away from the N pole of the compass and toward the S pole of the compass. So,
2.
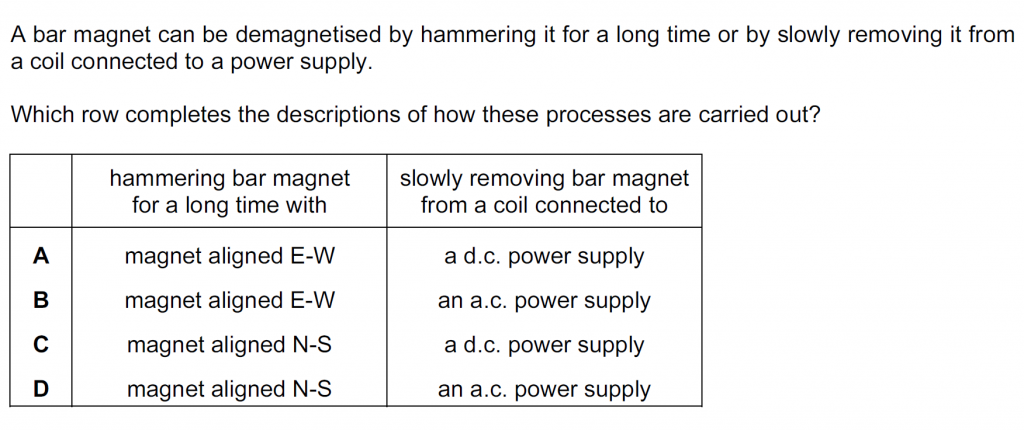
Answer : B
Solution
The magnet is demagnetised by hammering it to de-align the molecular magnets within the bar magnet, so,
3.
Answer : A
Solution
It is the electrons which are free and so carry the electric current.
4.
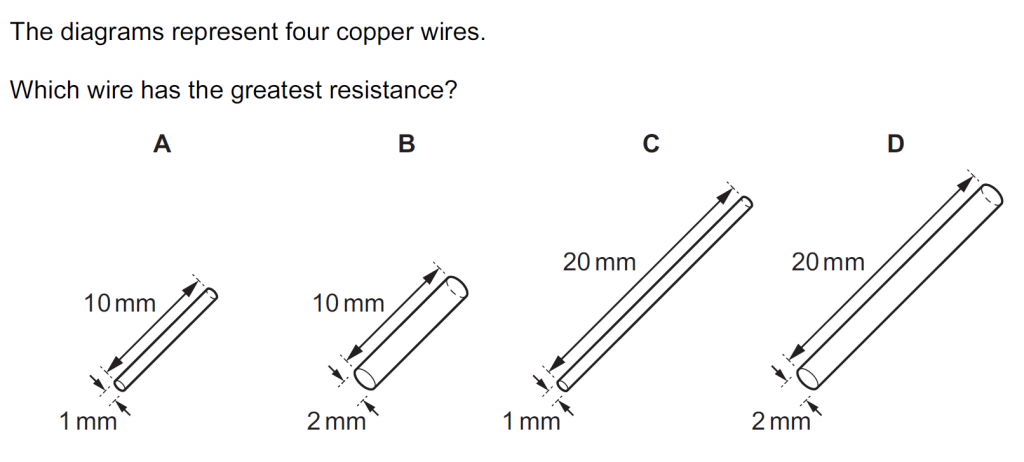
Answer : C
Solution
Longer and narrower copper wires have a greater resistance.
5.

Answer : C
Solution
The air-conditioning unit will absorb energy from the surroundings. The lamp and the electric fire will transfer all energy to the surroundings.
6.

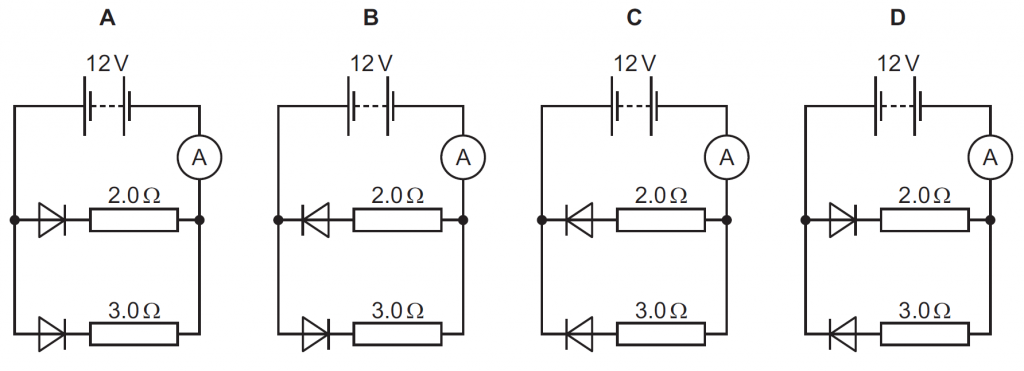
Answer : A
Solution
In Circuit A, both the diodes are forward biased so allow a large current to flow through them, thus the ammeter in A will show the greatest reading.
7.
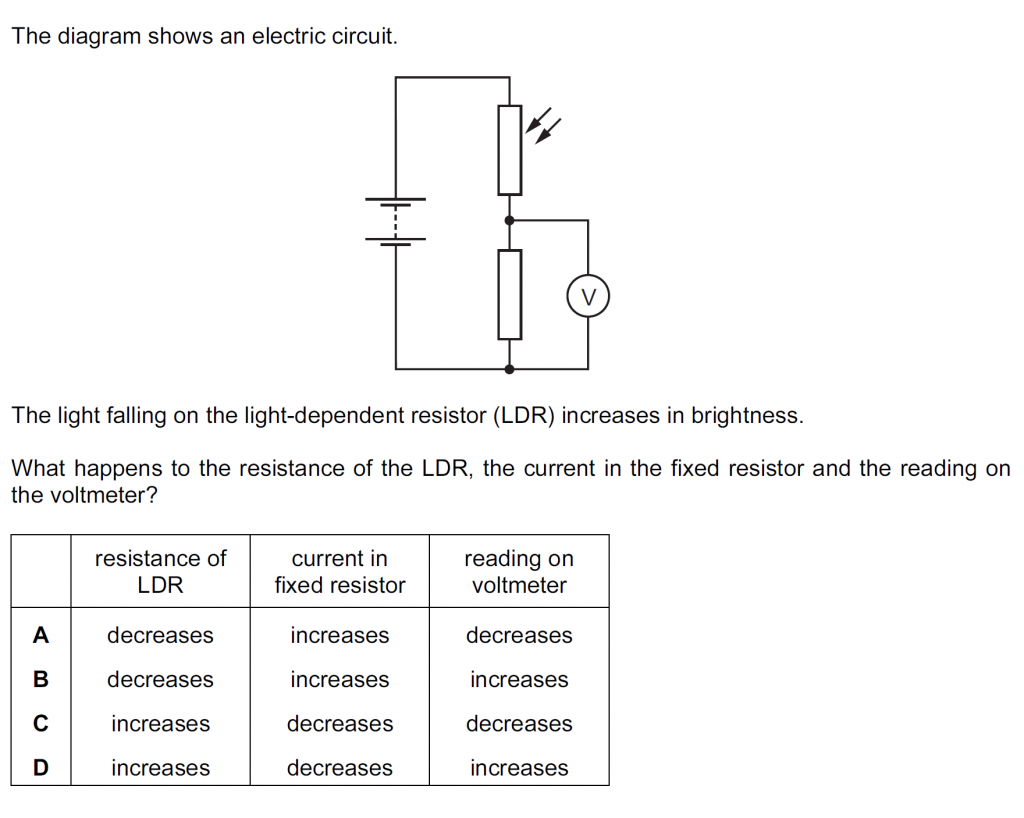
Answer : B
Solution
The increased brighter incident light will decrease the resistance of the LDR, increase the current in the fixed resistor as the total resistance then decreases, and that also increases the reading on the voltmeter.
8.
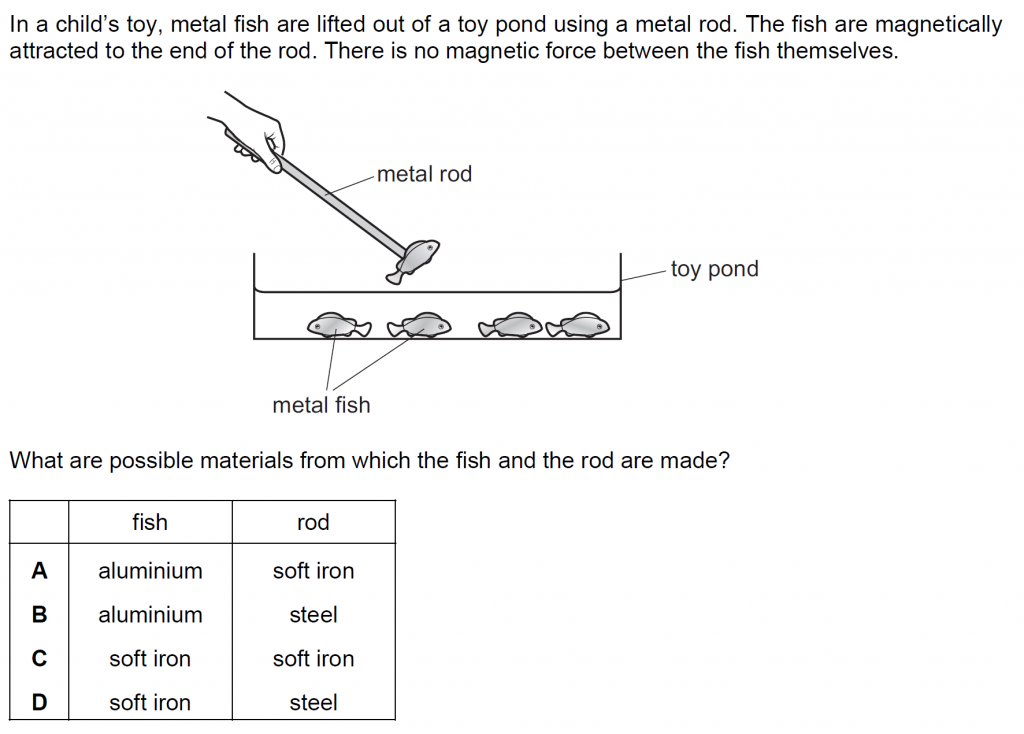
Answer : D
Solution
The metal rod is a permanent magnet, so made up of steel. The fish gets magnetised easily, so made up of soft iron.
9.

Answer : A
Solution
Method A, as the large alternating current will keep switching the magnetic field in opposite directions, rapidly, and thus be most effective in demagnetising the bar magnet.
10.

Answer : C
Solution
The current in the coil creates a magnetic field identical to a bar magnet, and will therefore attract the magnet placed near it.
11.

Answer : C
Solution
The rod becomes positively charged on losing electrons to the cloth on being rubbed.
12.

Answer : A
Solution
Electric Charge is measured in coulombs.
13.
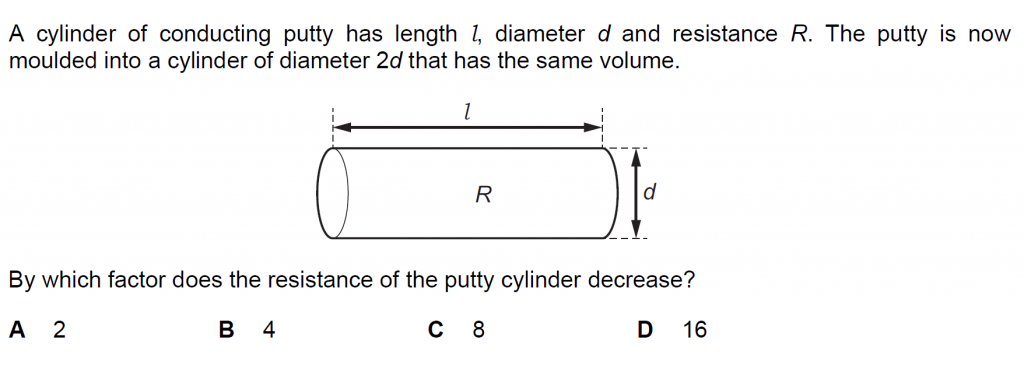
Answer : D
Solution
V = A x l
As the putty now is a cylinder of diameter 2d, its cross-sectional area is now 4 times, or A’ = 4A.
As the volume remains the same the length now will become, l’ = l/4.
Thus, the resistance depends directly on the length and inversely on Area, so, it is now, l’/ A’ = l/ (16A), or R/ 16. Thus, decrease by a factor of 16.
14.

Answer : C
Solution
Average e.m.f. = electrical energy supplied per unit charge, and is therefore, 3.0 x 108/ Q.
Q, the charge transferred is, Q = I t, where I is the current, so Q = 1.5 x 104 x 2.0 x 10-4 C = 3.0 C.
So, e.m.f. = 3.0 x 108/ 3.0 = 1.0 x 108 V.
15.
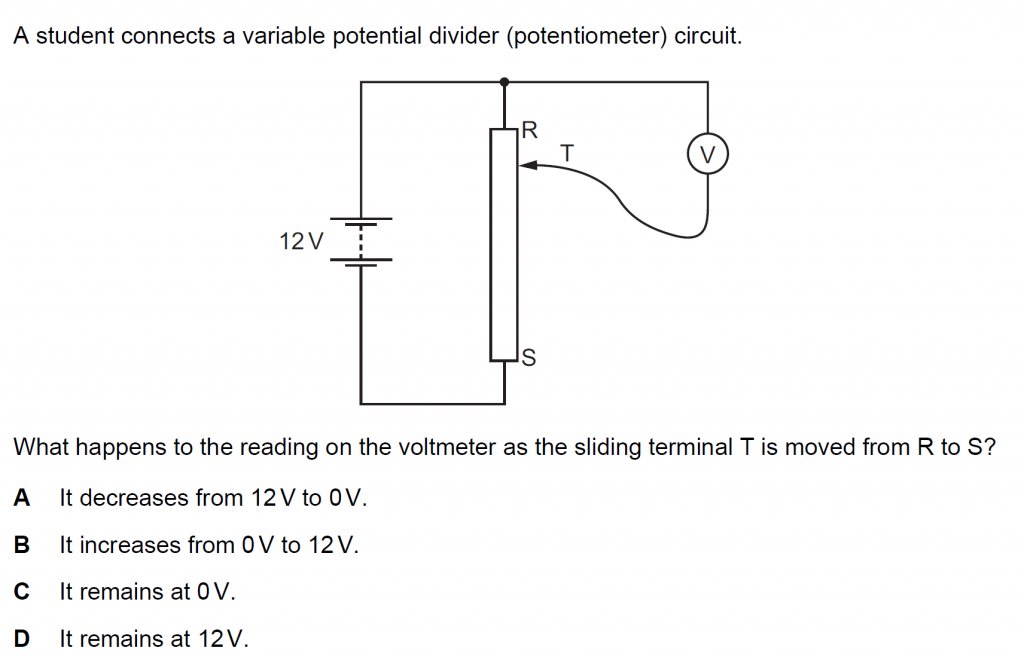
Answer : B
Solution
It increases from 0 to 12 V. As the potential difference across an electrical device is proportional to its resistance, which changes from 0 to maximum as the sliding terminal is moved from R to S.