Length

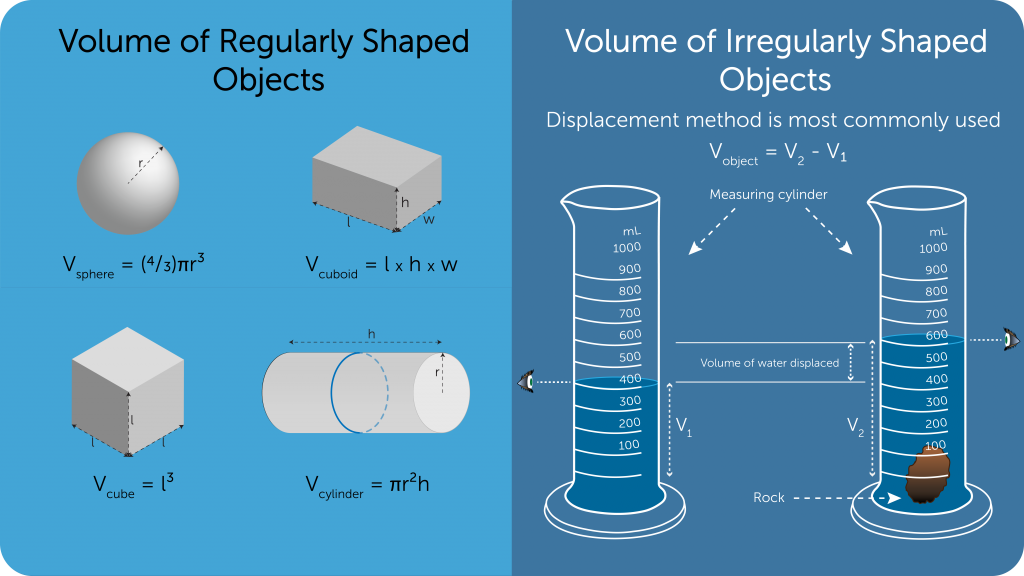
Volume
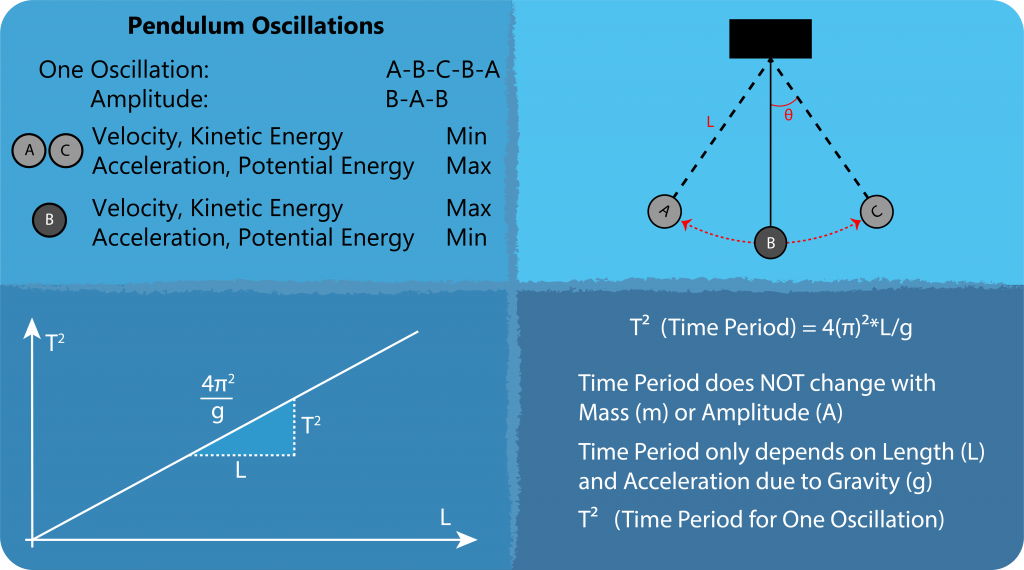
Pendulum
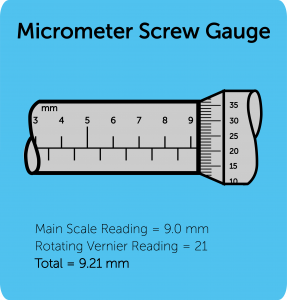
Micrometer screw gauge:
Least count: Least division on main scale/total number of divisions on circular scale
Total Value = Main scale reading + circular scale reading (Least Count)
Let’s look at a couple of examples:


Time:
Analogue and Digital devices:
- In analogue devices, the physical quantity is to be measured by using a pointer and scale system.
- Negative values cannot be measured,
- The range is small,
- The uncertainty is half the least count.
- In digital devices, the physical quantities are to be measured by using a display with binary system.
- The accuracy is high,
- Both positive and negative values can be measured,
- The range is large,
- The uncertainty is the least count.
Time period (T)
- It is the time taken by an object to complete one oscillation.
- I unit is seconds (s)
- For example, if ‘t’ is the time taken by a pendulum to complete 20 oscillations then the time period would be

Frequency (f)
- Number of oscillations completed by a particle or an object in 1 second
}&space;=&space;\frac{1}{\textup{time&space;period&space;(T)}})
- SI unit is rps (rotation per second) or Hertz (Hz), second inverse (
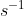 )
)





