Electromagnetic Induction
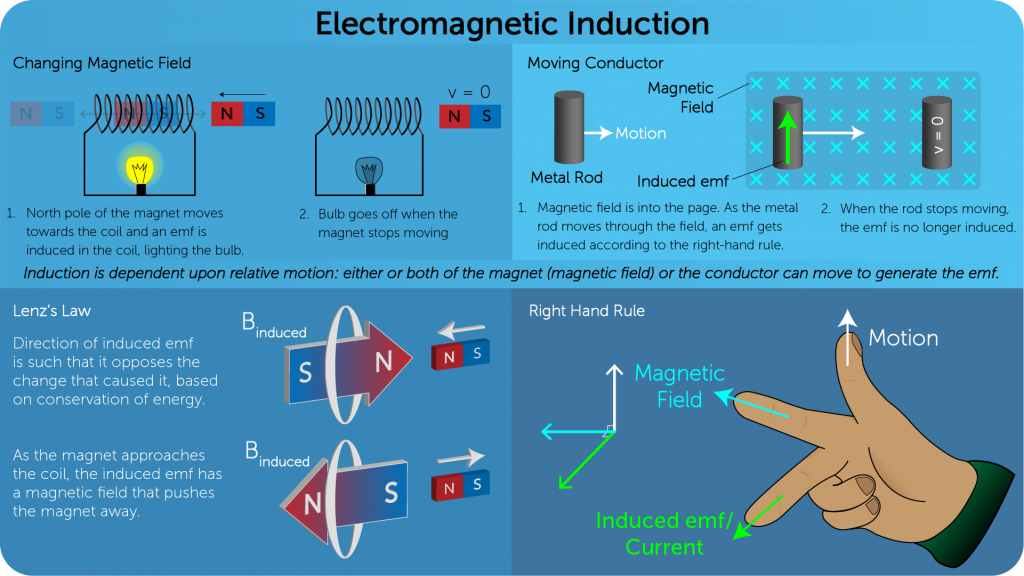
- Whenever a conductor is placed within a varying magnetic field, an emf gets induced and an induced current flows through the conductor.
Factors affecting the magnitude of the induced emf
The magnitude of induced emf is directly proportional to:
- Number of turns of the coil
- Cross-sectional area of the coil
- Magnetic field strength
- The relative velocity of the coil and the magnet
AC Generator
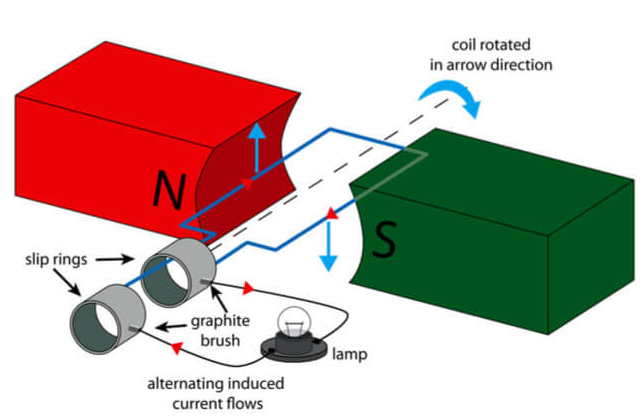
Source: powerplus.com
- The AC Generator consists of a rotating coil inside a stationary magnetic field connected to two sliprings that generate an alternating output.
- When the coil is vertical i.e. the angle between the normal of the coil and magnetic field lines is , as such the change in magnetic flux will be , hence the induced emf is .
- When the angle increases from to , the rate of change of magnetic flux becomes a maximum at , so the emf increases to maximum at .
- When the angle increases from to , the rate of change magnetic flux decreases to at , hence the induced emf is at is
- When the angle increases from to , the rate of change of magnetic flux increases to maximum, so the emf increases to a maximum at , however in the opposite direction.
- When the angle increases from to , the rate of change of magnetic flux decreases to 0, so induced emf at is 0.
- Therefore, nature of the induce emf is alternating, following a sinusoidal pattern.
Transformer
 ,
, 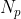 ,
,  , and
, and  ,
, 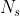 ,
,  are the electric current, number of turns, and emf in the primary and secondary circuit, respectively.
are the electric current, number of turns, and emf in the primary and secondary circuit, respectively.
Primary circuit:
- An AC source is connected in the primary circuit.
- The AC current through the primary coil produces an alternating magnetic field.
Soft-Iron core:
- The permeability of soft iron is the extremely high and is used to link the magnetic field between the primary and secondary coils.
Secondary circuit:
- The changing magnetic field at the secondary coil produces an alternating current in the secondary circuit.
- So, power is transferred from the primary circuit to the secondary circuit.
- The emf and current in the secondary can be altered by changing the ratio of the number of turns in the secondary and primary coils.
- A step-up transformer has more coils in the secondary circuit, and a step-down transformer has fewer coils in the secondary circuit.
Transformer equations relating N, I, and V
- From Faraday’s laws:
- For an ideal transformer (100% efficiency):
Step-up transformer:
Step-down transformer:
E.g. 

High voltage transmission lines:


- By using a step-up transformer, V can be increased, decreasing I.
- Thus
 , can be minimized.
, can be minimized.
- Cost–effective as a thinner cable can be used to carry the reduced current.
Force on Moving Chargers
A uniform field means magnetic field line are parallel.
Force on a current carrying conductor
Force (F) on the conductor of length (L) carrying a current (I) moving through a magnetic field (B):0
4.6.5 DC Motor
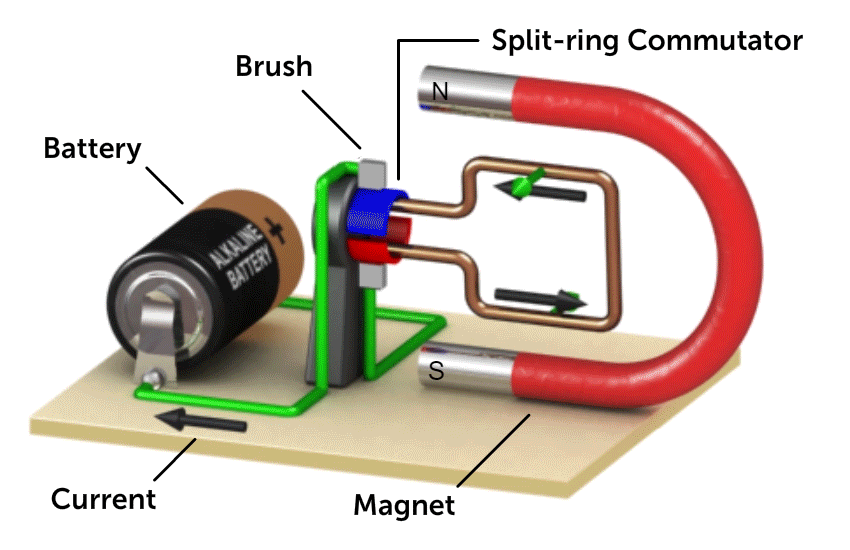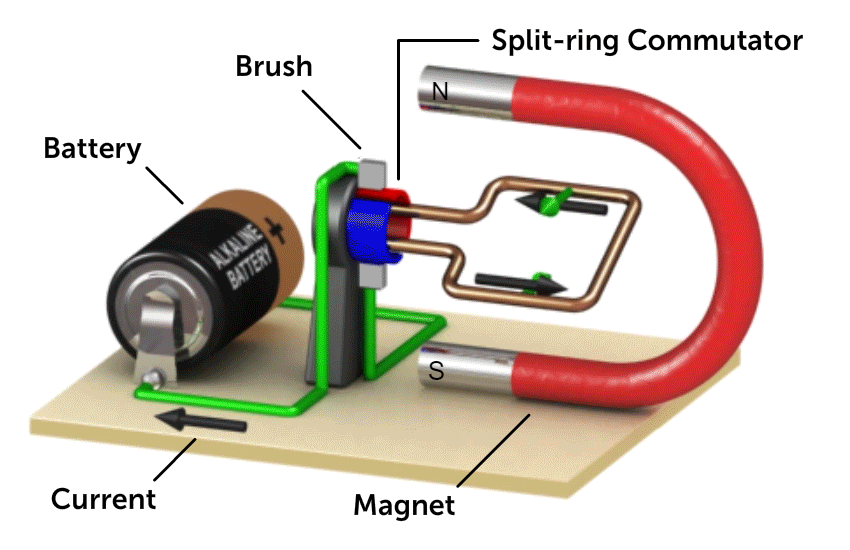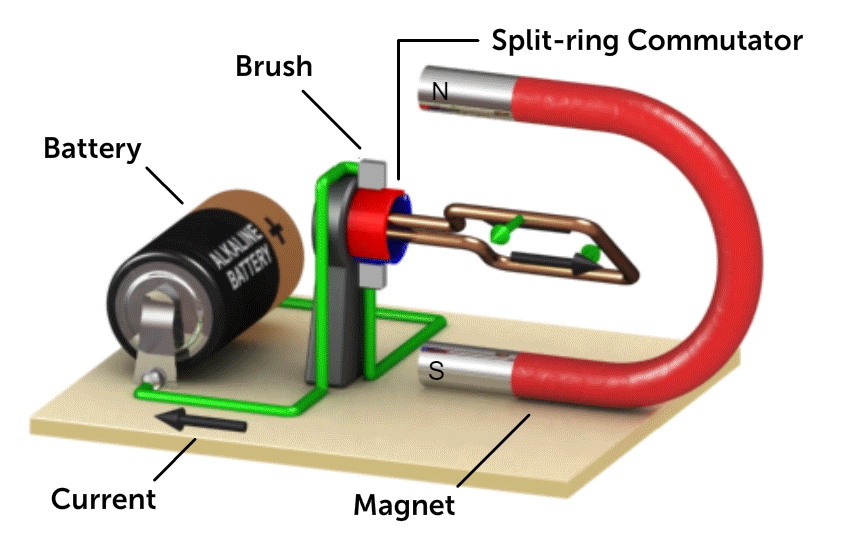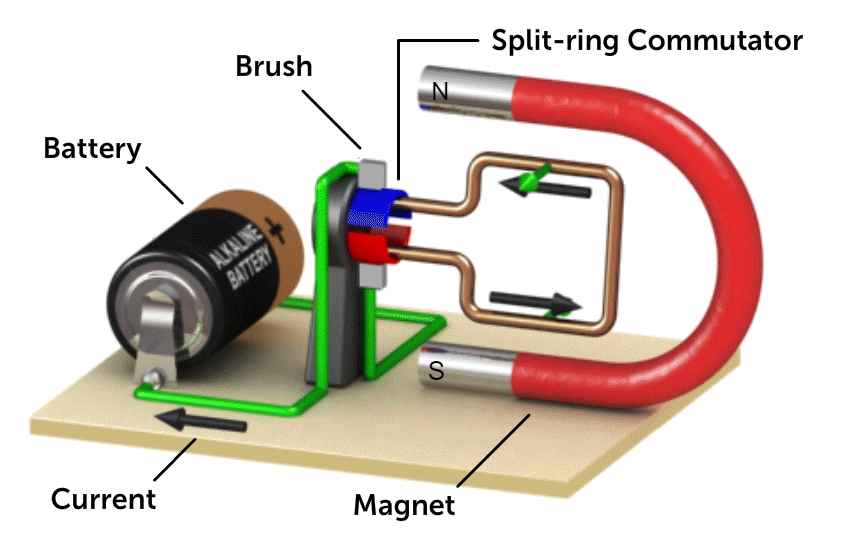
Source: National Mag Lab
The turning effect is directly proportional to
- No of turns of the coil
- Electric current
- Magnetic field strength
- Area of the coil



