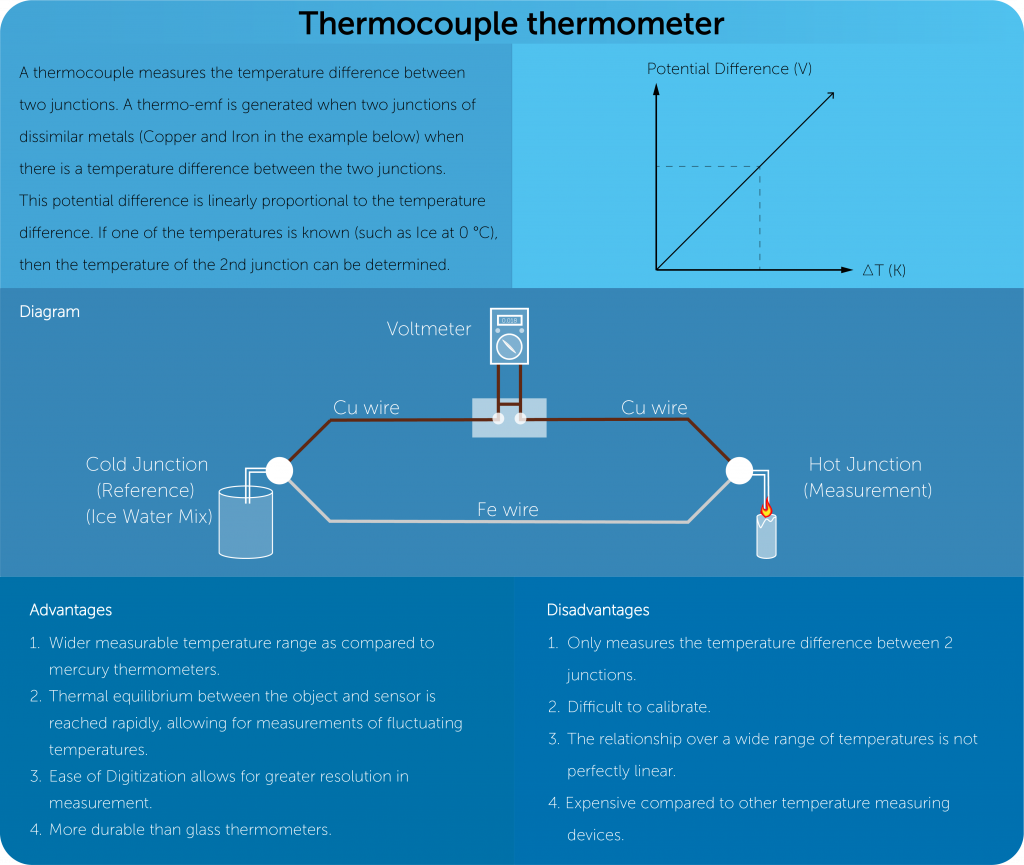
Measurement of temperature
- To measure the temperature of a substance, some of its physical properties should vary with temperature; they are the thermometric properties.
- These properties could be volume, pressure, resistance etc.
- For these physical properties, there should be some lower and upper fix points.
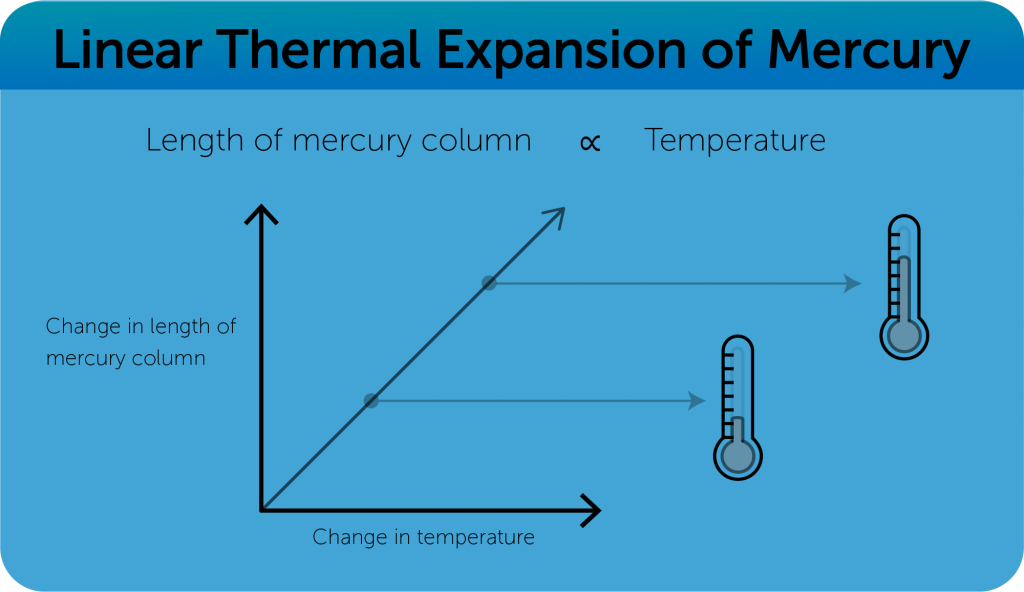
Mercury in glass thermometer
- Volume of Mercury ∝ Change in temperature.
- Lower fix point —–melting point of ice (0 ̊C)
- Upper fix point —–boiling point of water (100 ̊C)
Sensitivity
- It is the length of increase of the liquid per degree rise in temperature.
- More sensitive means more noticeable expansion.
- Sensitivity increases with decrease in diameter of the bore.
Range
It refers to the scope of temperature it can measure, or it is the minimum to maximum measurable temperature by a thermometer.
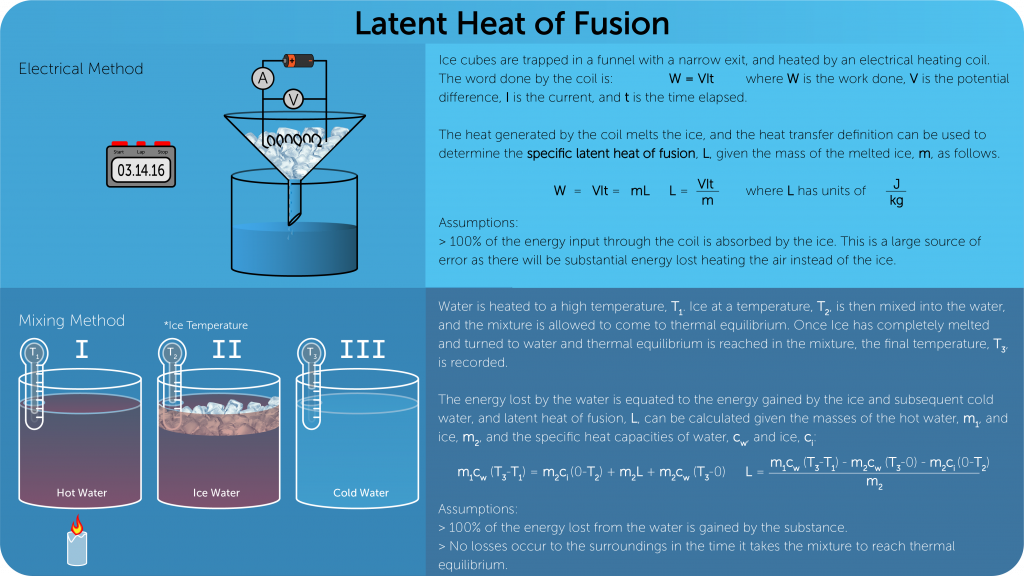
Specific heat capacity
- Amount of energy needed to increase the temperature of one kilogram of a substance by one degree Celsius.

- Q = Energy (J)
- m = mass (Kg)
- ΔT = change in temperature (Co or K)
- SI unit →
 or
or 
Thermal capacity (or Heat Capacity)
- Amount of energy needed to change the temperature of a given mass of a substance by 1 ̊C.

- SI unit is
 or
or 



- Heat capacity = mass x specific heat capacity
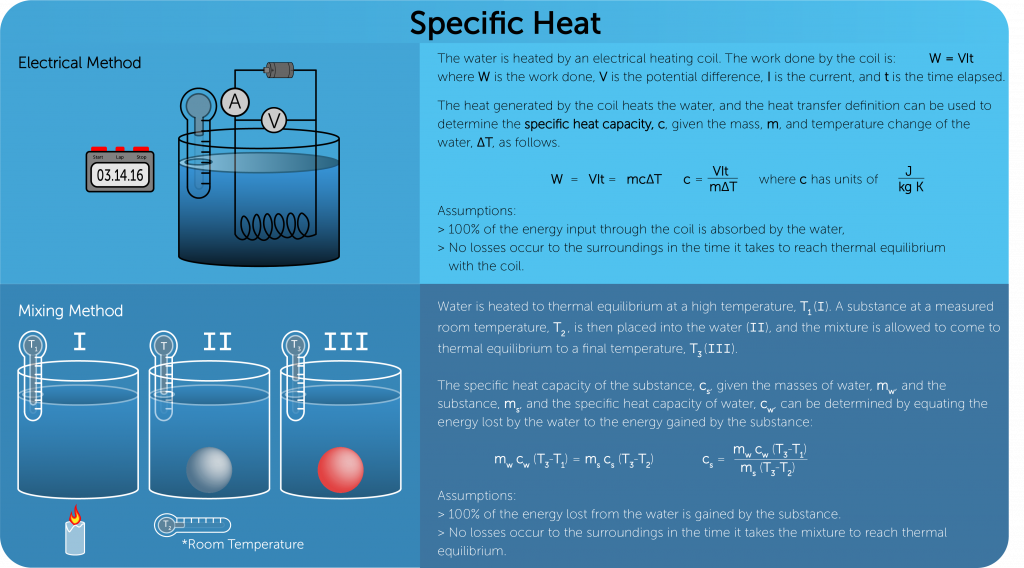
Phase Change:
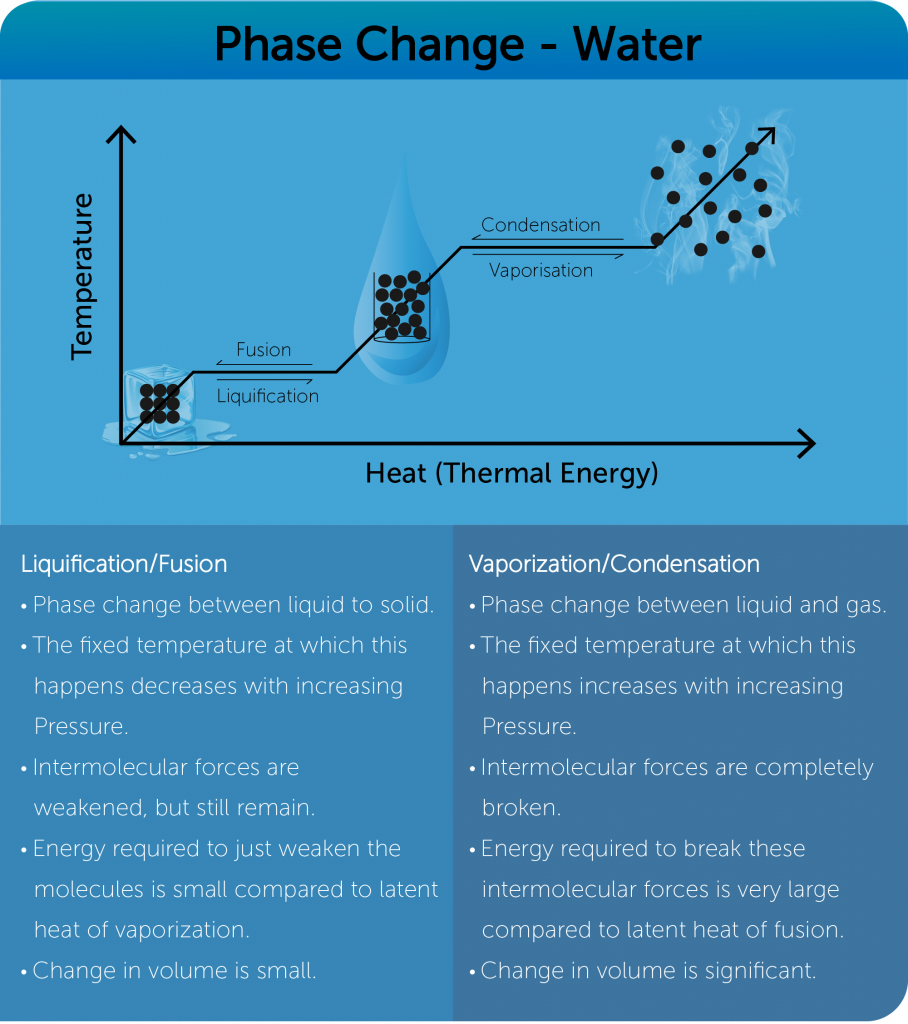
Specific latent heat
- Amount of energy required per unit mass to change the phase of a material.
Specific heat latent of Fusion/Liquification
- Amount of energy needed to change the phase of one kilogram of a solid to liquid at constant temperature.

- SI unit is

Specific heat latent of a Vaporization/Condensation
- Amount of energy needed to change the phase of one kilogram of a liquid to gas at constant temperature.

- SI unit is