Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : BSolution
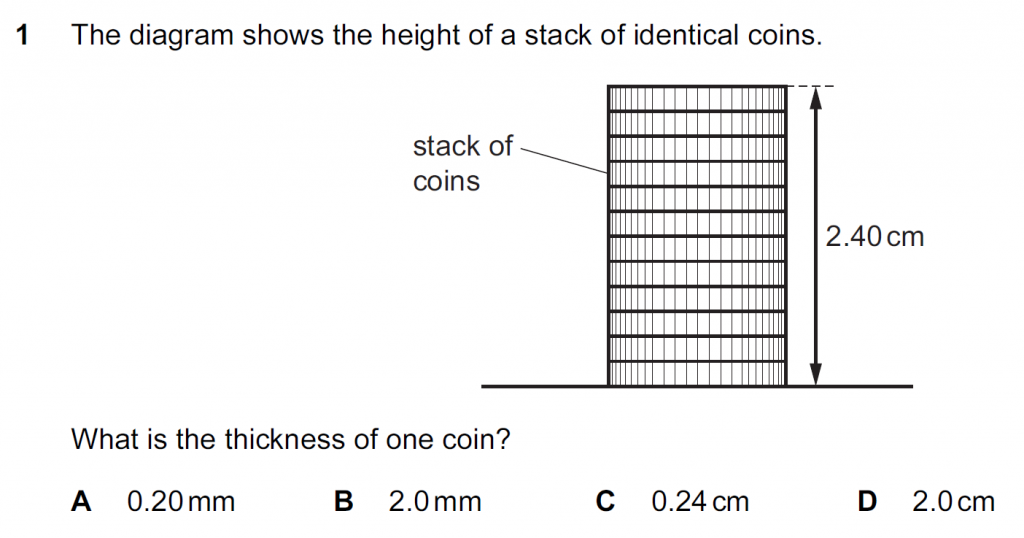
From the diagram, there are 12 coins stacked one on top of the other. They contribute together to a height of 2.40 cm.
If the thickness of one coin is t, then
12 t = 2.40 cm
And,
t = 2.40/ 12 = 0.20 cm
And because 1 cm = 10 mm
t = 0.20 x 10 = 2.0 mm
Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : DSolution
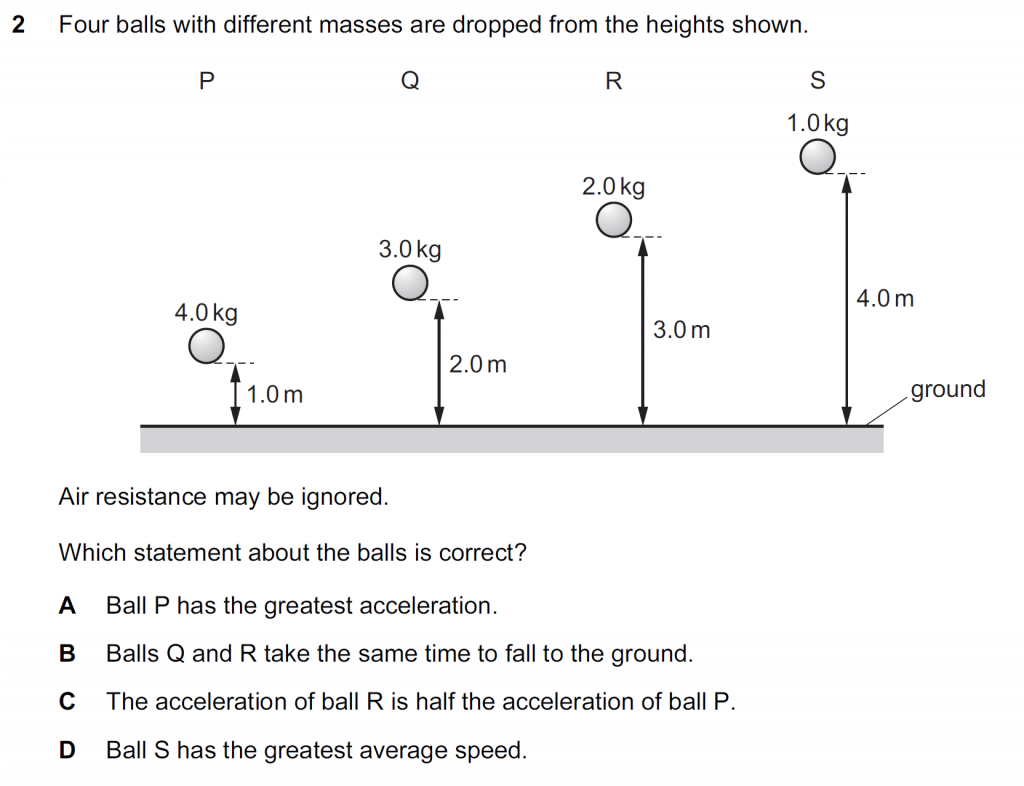
- All balls, in the absence of air resistance fall with the same acceleration; the acceleration due to gravity = g. So, choice A is wrong.
- Time to fall is given by the kinematics equation
S = ut + 0.5 a t2
For initial velocity u = 0, and a = g,
S = 0.5 g t2
Because, ball Q covers a shorter height of 2.0 m, compared to ball R, which covers a greater height of 3.0 m, so ball R will cover a longer time t. So, choice B is wrong.
- All balls have the same acceleration, as this is free fall, with no air resistance. So, choice C is wrong.
- Average speed = (initial speed + final speed)/ 2
Initial speed = 0.
Final speed, is v, where, v = (2 g h)0.5
Because h is the height fallen, and S falls the greatest height of 4.0 m, the final speed of S is the most, and so the Average speed of S is the greatest.
Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : BSolution
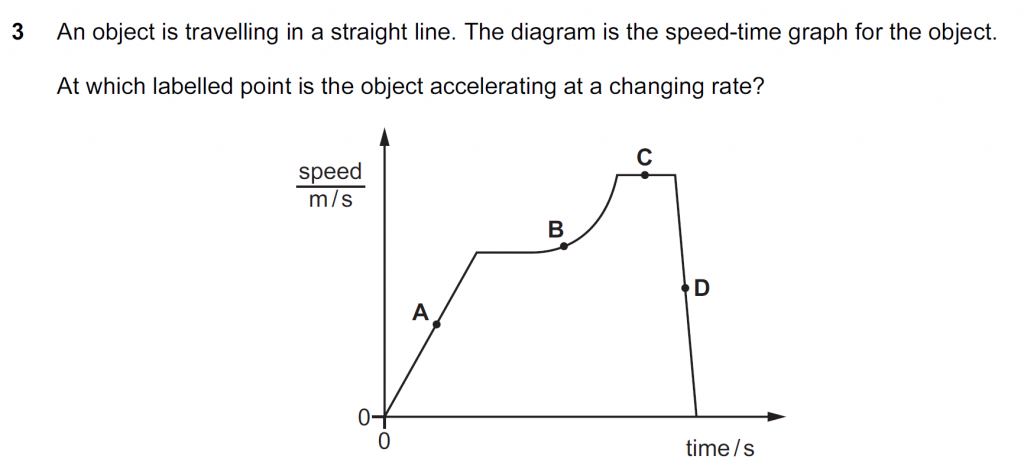
Acceleration is rate of changing of velocity, so it is equal to the slope of the speed – time graph.
In the graph above the slopes of the speed – time graph is constant during A, C, and D. So, the accelerations are not changing there. The slope is changing during B, so object’s acceleration is changing at the labelled point B.

Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : BSolution
- A balance can be used to compare masses as well as weights. If the balance is balanced, it would mean the objects on the two pans have the same weight and the same mass, as m1 g = m2 g, so m1 = m2.
- Heavy objects have a greater Weight W, which is equal to mg, thus implying a larger mass m, than that of the lighter ones.
- Large objects imply a larger volume. However, a larger volume object can have a smaller mass if its density is adequately lesser than that of the smaller one.
- Weight is a force, the force of gravity on an object. Mass is a measure of inertia and is not a force.

Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : BSolution
W = mg
Weight changes from point to point, because mass is a constant but the gravitational field strength g varies.
At the height of the space probe:
W = mg
3.5 = m x 7.0
m = 0.50 kg
This mass will remain constant and will remain the same at the Earth’s surface.
Weight at the Earth’s surface = m g = 0.50 x 10 = 5.0 N, where g here is the gravitational field strength on the Earth’s surface.

Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : ASolution
A: She opens the parachute when she reaches a steady vertical speed, that is when her weight = Air resistance. Her weight W does not change on opening of the parachute, however the air resistance on her, upward, due to the opened parachute becomes a lot more, resulting in a net upward force, and so an upward acceleration.
B: Her weight is non-zero, as the Earth very well continues to exert a gravitational force on the skydiver. The net force on her which W – air resistance = 0 N, as she falls at a steady speed with a 0 acceleration, so a 0 N net force.
C: If she accelerates the resultant force on her is nonzero, from Newton’s second law. F = ma, if a is nonzero, the net force F on her will also be non-zero.
D: Air resistance depends on the fact that there is air, and the object is moving all the way through the air with a nonzero velocity. So, as she falls at a steady speed the air resistance is nonzero.
Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : CSolution
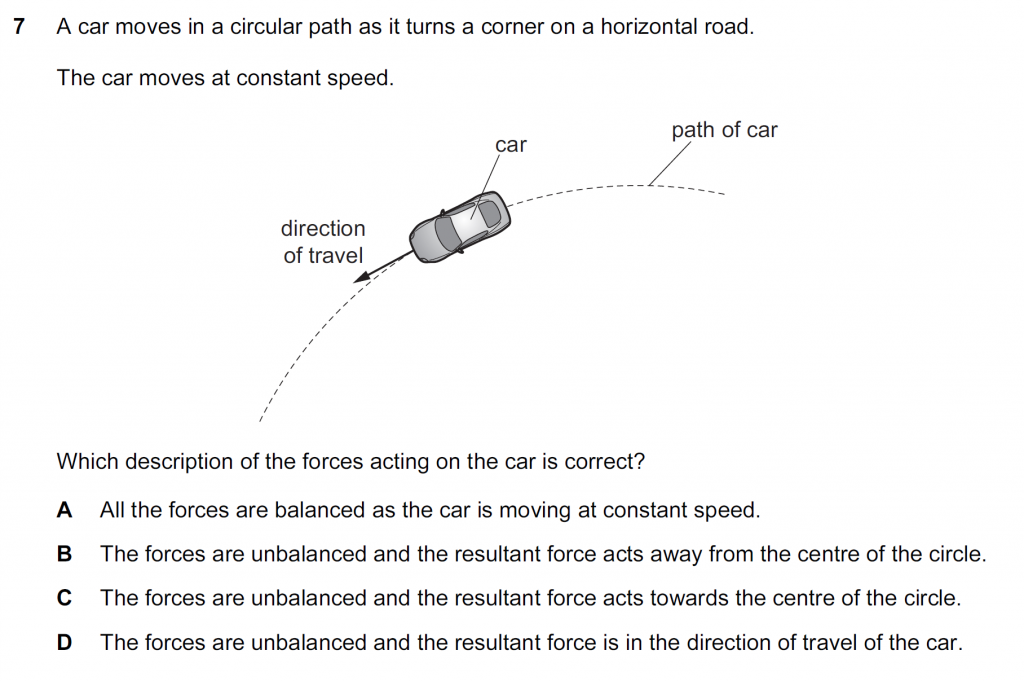
A: The car is moving at a constant speed but in a changing direction on the circular path, so is accelerated. The vector acceleration will change if speed or/ and direction will change. So, if the acceleration is nonzero, the forces are not balanced.
B: The unbalanced forces will act toward the centre of the circle as the net force has to provide a centripetal force toward the centre. This is the make sure that it curves inward.
C: Is right.
D: If the resultant force is in the direction of travel, the car will speed up, however the car as given in the question, moves at constant speed.
Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : CSolution
Change of momentum will have the same unit as momentum, as only quantities of the same units can combine. So, Force = Rate of change in momentum = Change in momentum/ time.
So, change in momentum = Force x time and will have the units N s
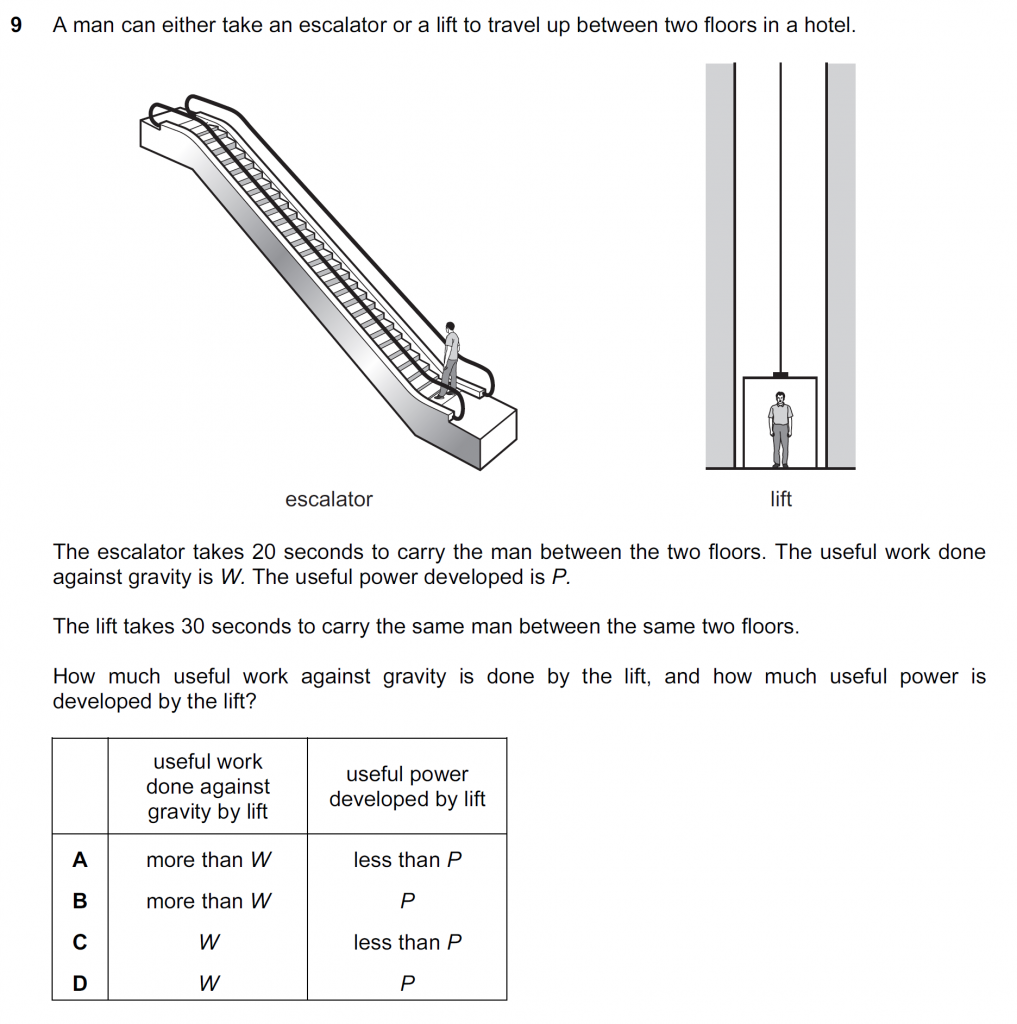
Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : CSolution
Useful work against gravity depends on how high you take the man. Because both the lift and the escalator take the man the same height, the useful work against gravity is the same = W. Useful power developed is useful work done/ t. Because the lift takes a greater time than the escalator, it develops a lesser power than the escalator, which is P.

Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : BSolution
Efficiency = Useful Power output/ Power input
Useful power output = Power input – Power wasted; power wasted = Energy wasted/ time taken = 34 J/ 1 s = 34 W.
Useful power output = 40 – 34 = 6 W.
Efficiency = (6/ 40) x 100 = 15 %

Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : DSolution
Pressure due to the column of liquid = Force due to the column of liquid/ Cross section of the column of liquid = Weight of the column of liquid/ A = mg/ A. mass of the column of liquid m = Its Volume V x density ρ, m = V ρ. And V = height of the liquid column h x cross section of the liquid column A. V = A h. So, m = V ρ = A h ρ
P = mg/ A = (A h ρ g)/ A = ρ g h
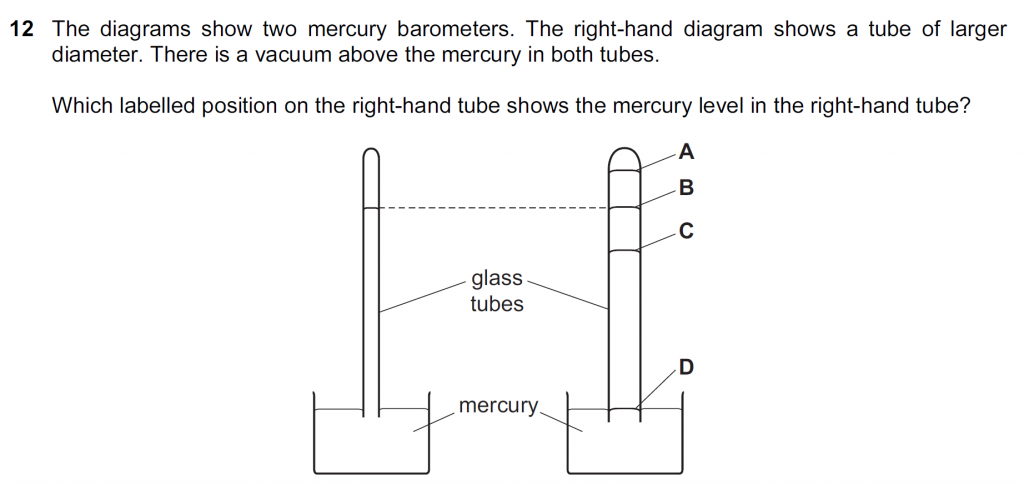
Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : BSolution
The mercury barometer gives the atmospheric pressure, which is the same in the location of both the tubes. The atmospheric pressure = pressure of the mercury column balancing the atmospheric pressure, and pressure of the mercury column = ρ g h, where h is the height of the mercury column.
So, because the pressure is the same at the location of both the tubes, the height of the mercury column is the same, so, B is the right answer.
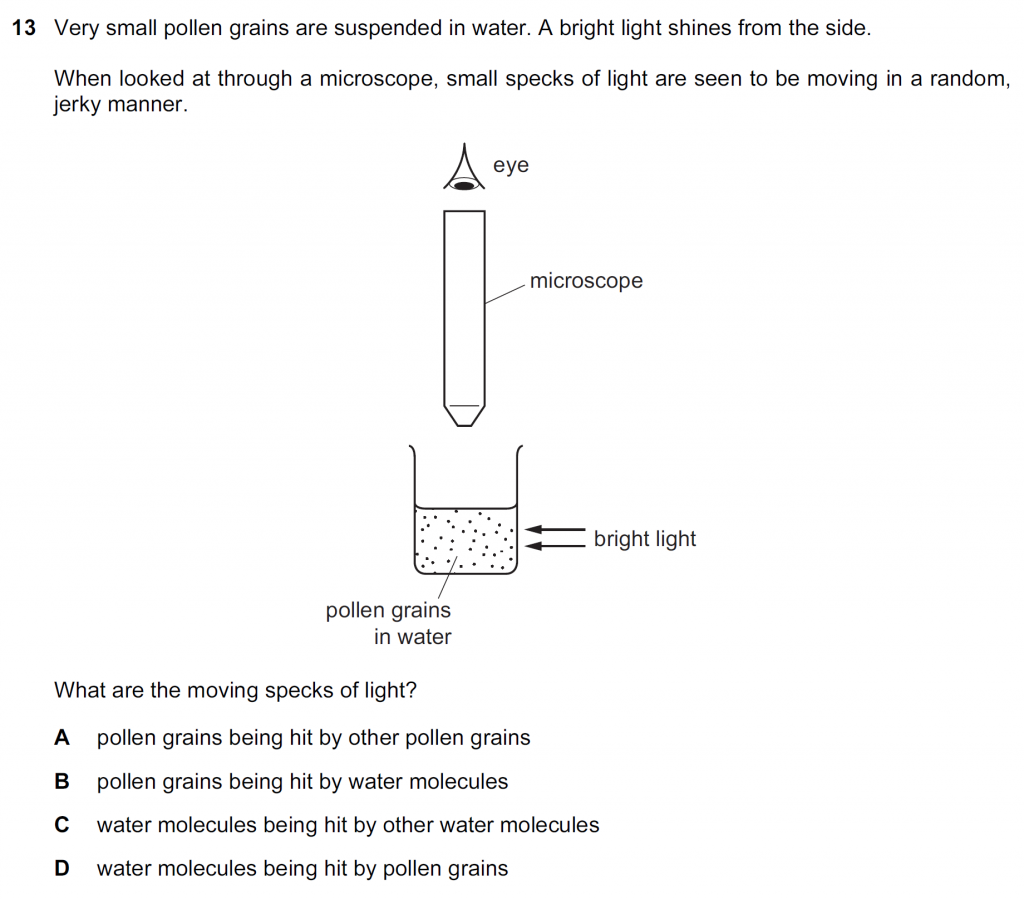
Click to Show / Hide Solution
Answer : BSolution
This is an illustration of Brownian motion. This shows a random jerky motion of suspended pollen grains as they are hit by the moving water molecules from all sides randomly. These collisions result in net unbalanced forces on the pollen grains which therefore move in random jerky motion as visible as moving specks of light. So, B is the right answer. The water molecules are too small to appear as specks of light even though they collide with other water molecules, and with pollen grains.

F = 56 000 N = m a = 16 000 kg x a, as the force is constant, the acceleration a is constant.
a = F/ m = 56 000/ 16 000 = 3.5 m s-2
v = u + at, we can apply this equation as the acceleration is constant
v = 0 + 3.5 x 16 = 56 m/ s
Speed = 56 m/ s.

Momentum = mass x velocity. It is a vector quantity because it has a direction. Velocity on which it depends has a direction and is a vector.
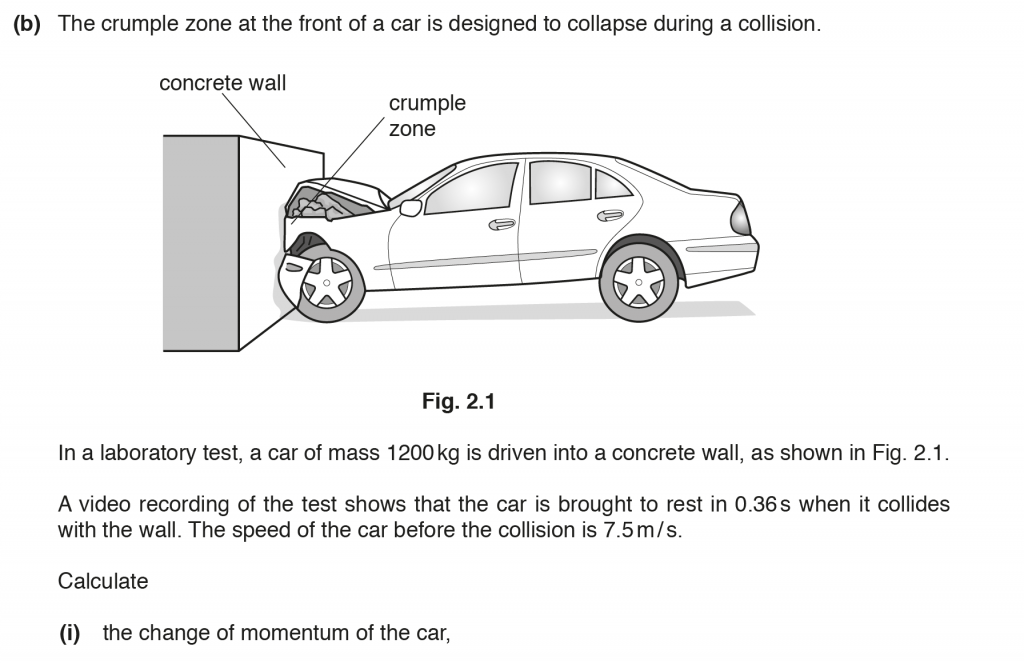
Change in momentum = mass x (final velocity – initial velocity) = 1200 x (0 – 7.5) = – 9000 kg m/ s
Change in momentum = – 9000 kg m/ s.

Average force on the car = change in momentum of the car/ time taken = 9000/ 0.36 = 25 000 N
Average force = 25 000 N

Energy absorbed by the crumple zone = all the energy transferred during the collision = kinetic energy of the car = (1/ 2) mv2 = 0.5 x 1500 x v2 = 4.3 x 105
v = 23.94 = 24 m/ s.

More damage will occur.

The resultant of all the forces acting on the object is 0 N.
The resultant force = 0 N

The moments of all the forces acting is 0 N m.
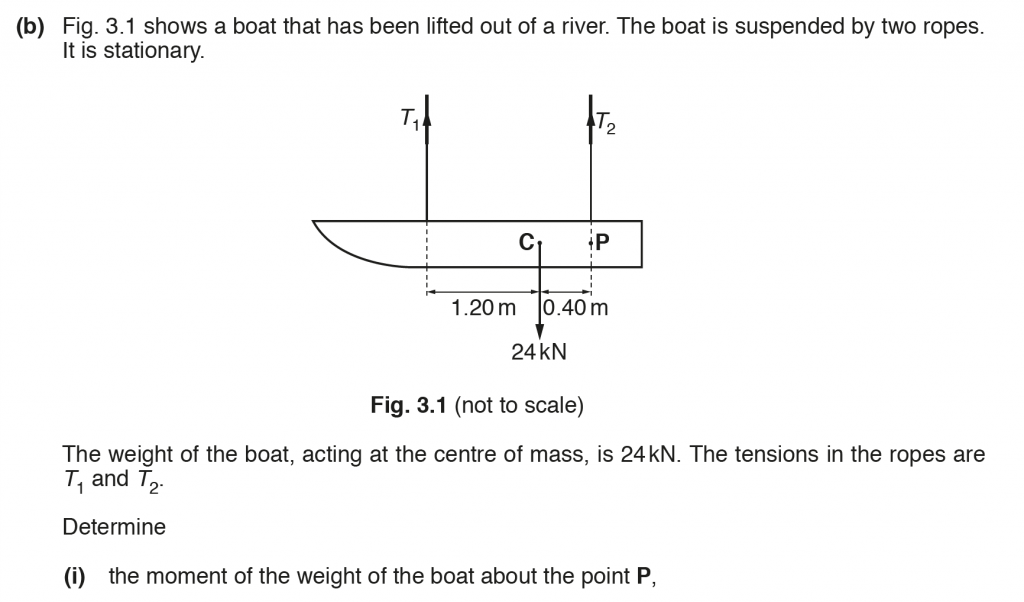
Moment of a force about a point = Force x perpendicular distance from the point to the force
Moment = Weight x CP, where C is where the weight W acts and P is the point about which we want the moment.
Moment = 24 000 x 0.40 = 9600 N m
Moment = 9600 N m, counter clockwise

Taking moments about P and equating clockwise moment = counter clockwise moment.
T1 x (1.20 + 0.40) = 24 000 x 0.40
T1 = 6000 N, Upward

Net force = 0 N
W = T1 + T2, T2 = W – T1 = 24 000 – 6000 = 18 000 N
T2 = 18 000 N, Upward
























