
Answer : A
Solution
The most accurate and precise method of measuring a physical quantity is by using a measuring instrument of the smallest least count.
A: is the right choice here as it is a length measuring instrument of lesser least count than the meter rule. Its least count is 0.01 mm, a ruler’s least count is 1 mm.
B: Least count = 1 mm
C: A top pan balance measures mass, not length.
D: The displacement method measures Volume, not length.
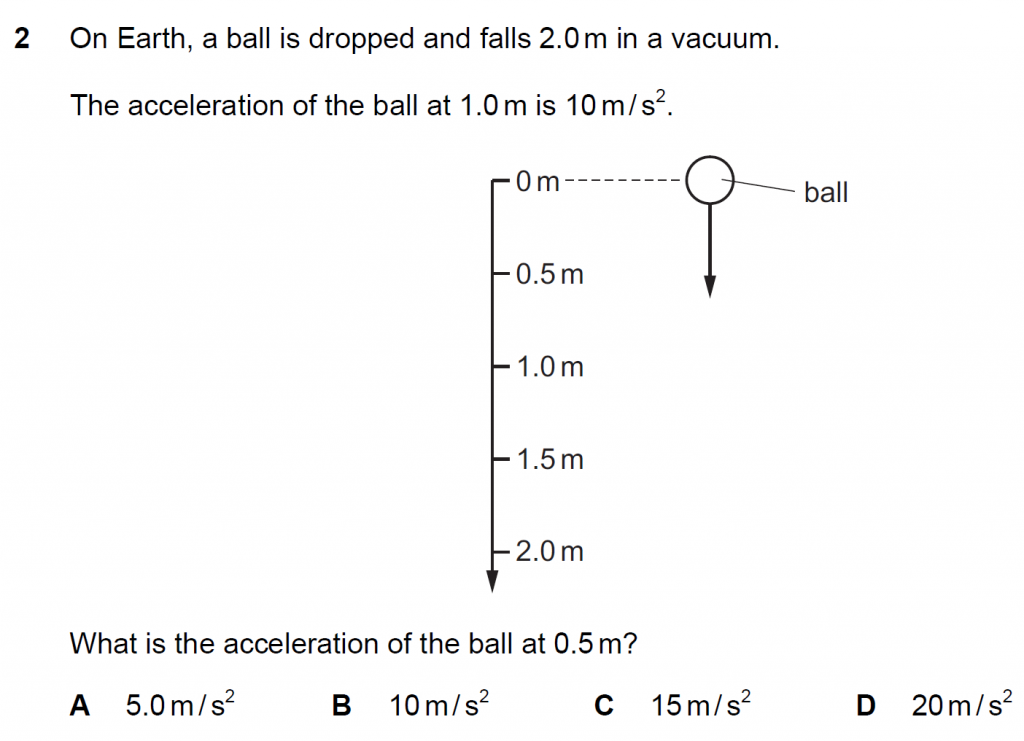
Answer : B
Solution
Acceleration of a ball falling on Earth will remain the same over short distances like here So acceleration = 10 m s-2.

Answer : B
Solution
A: Weight will not change as it is due to the masses of Earth and the skydiver which is not changing.
B: The sharp increase in upward force due to air resistance on the parachute will result in an upward acceleration.
C: The skydiver slows down due to the net upward force.
D: The acceleration is upward, but the velocity and movement is downwards only.

Answer : C
Solution
A: Mass is unchanging.
B: Mass is unchanging.
C: Yes, it weighs less on the Moon than on the Earth, as the gravitational field strength on the Moon is smaller than on the Earth, and W = mg
D: It weighs lesser.
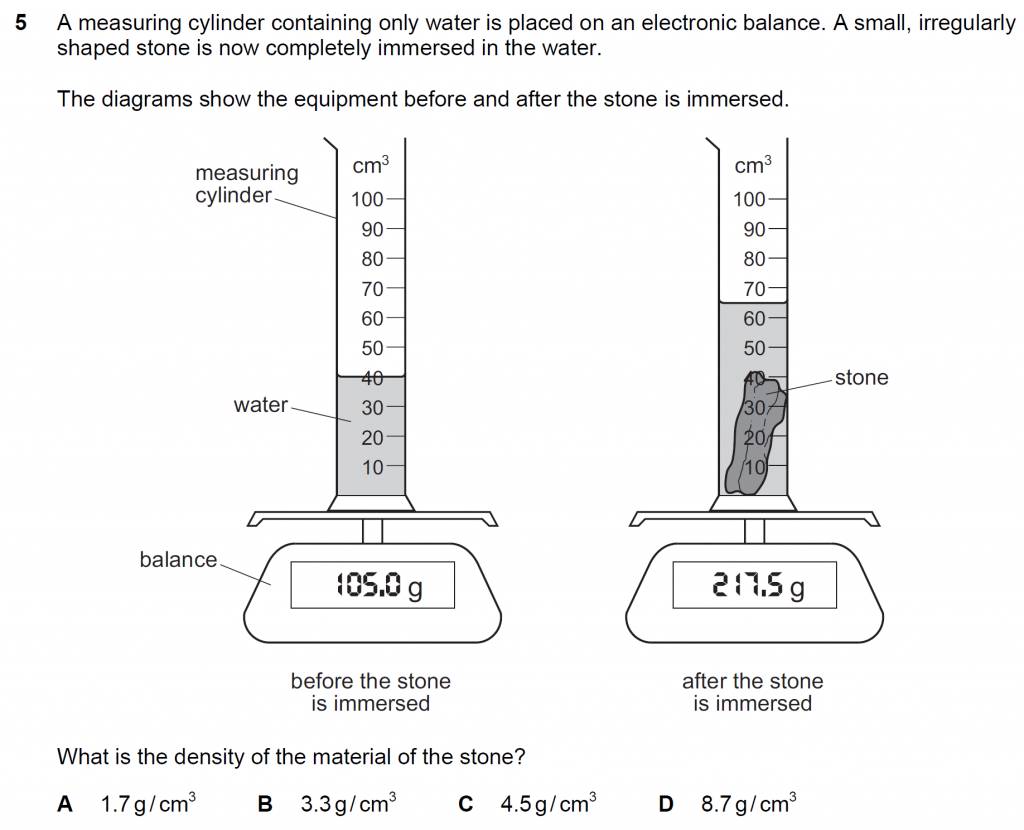
Answer : C
Solution
Density of the material of the stone = mass/ volume
Mass of stone m = Mass of the measuring cylinder with water and stone – mass of the measuring cylinder with only water = 217.5 – 105.0 = 112.5 g
Volume of the stone V = Volume of water and stone – volume of just stone = 65 – 40 = 25 cm3
Density m/ V = 112.5/ 25 = 4.5 g/ cm3.

Answer : D
Solution
Steady speed in a straight line implies a constant velocity and therefore a 0 acceleration and a 0 N resultant force.
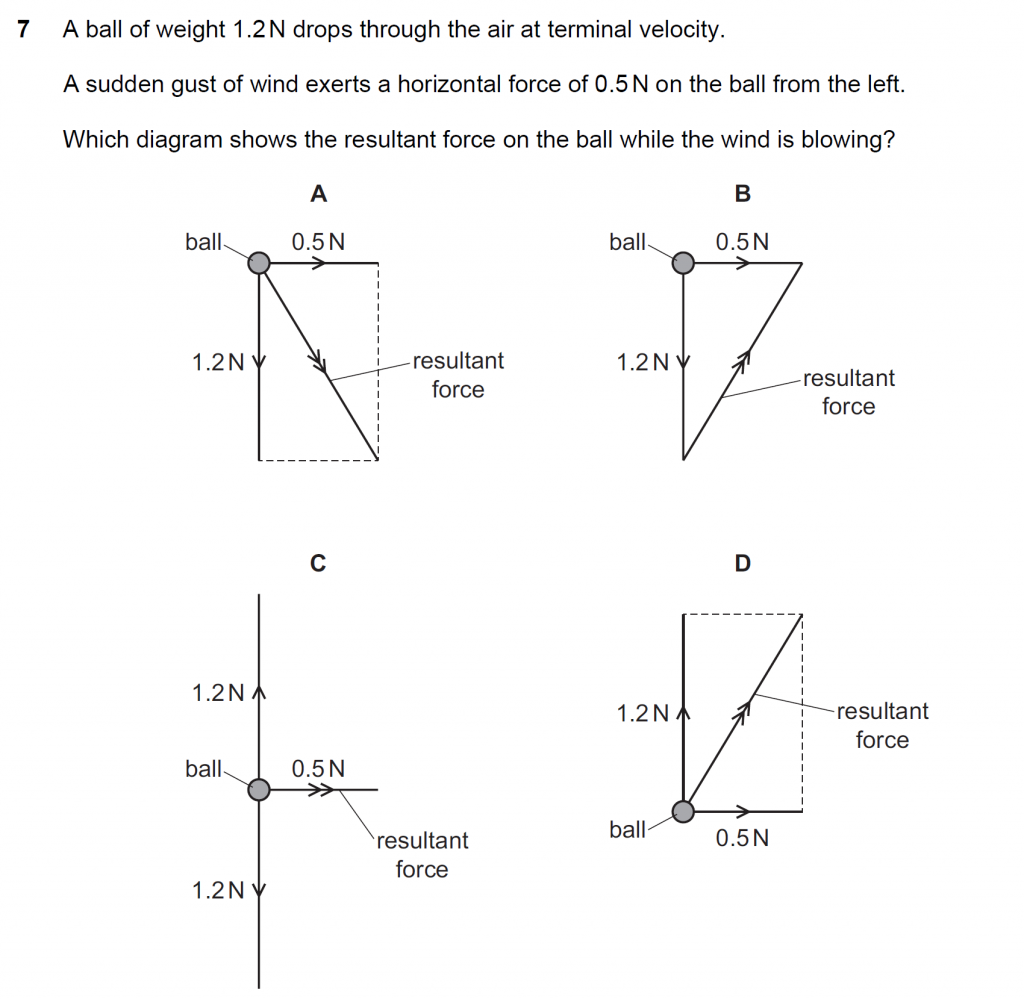
Answer : C
Solution
A: Because the ball drops vertically through the air at terminal velocity, the net force on it in the vertical direction is 0 N, so choice C is right. Only a horizontal resultant force due to the gust of wind.

Answer : B
Solution
Weight of the uniform bridge acts on its centre of gravity at 2.0 m from the pivot. The lifting force F just begins to lift it, overcoming the clockwise moment of the weight of the bridge.
F x 4.0 = 10 000 N x 2.0
F = 5000 N

Answer : A
Solution
Applying conservation of momentum to this perfectly inelastic collision,
Momentum of bullet + Momentum of stationary wooden block = Momentum of bullet + block
0.10 x 600 + 0 = (0.10 + 1.90) x V
60 = 2.00 V
V = 30 m/ s.
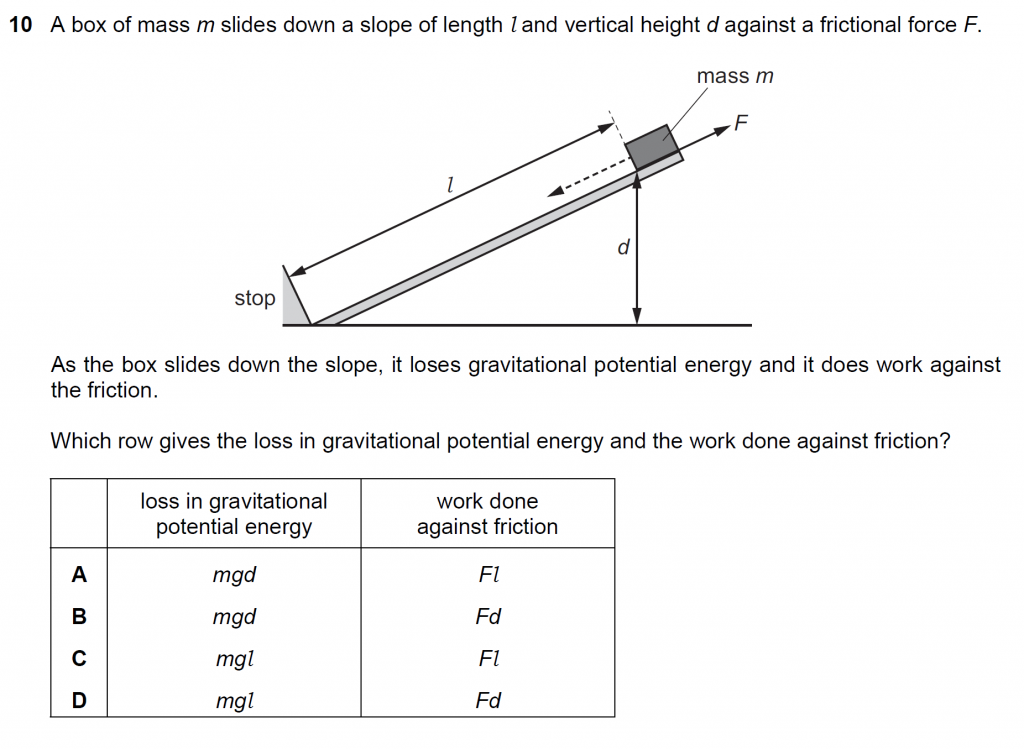
Answer : A
Solution
Loss in gravitational potential energy = m g (Initial height – final height) = m g d
Work done against friction = Force of friction x slope of length l = F l
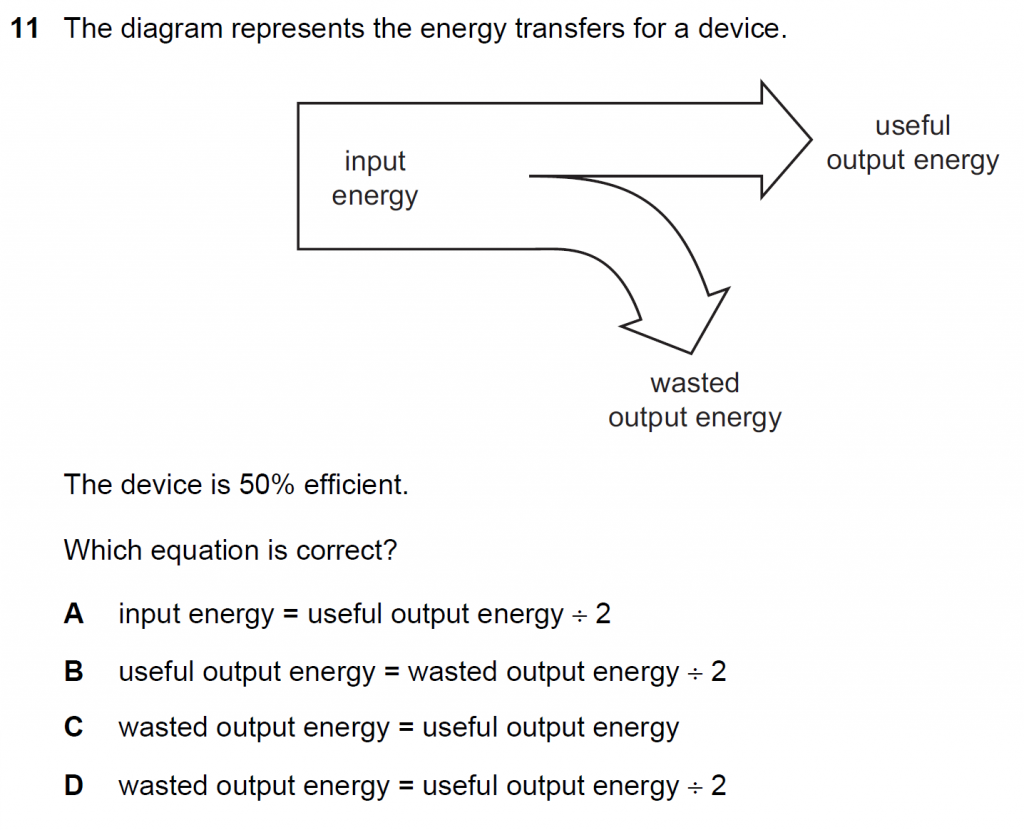
Answer : C
Solution
Efficiency = Useful output energy/ Input energy
50 % = Useful output energy/ Input energy
1/ 2 = Useful output energy/ Input energy
Input energy = 2 x Useful output energy
Useful output energy = Input energy – wasted output energy
Useful output energy = 2 x useful output energy – wasted output energy
Wasted output energy = 2 x useful output energy – useful output energy
Wasted output energy = useful output energy
Also from the diagram this is very evident.

Answer : C
Solution
A: W = F d = 10 x 1 = 10 J
B: 4 x 1 = 4 J
C: 20 x 2 = 40 J
D: 2 x 2 = 4 J
Most work done is in the process C.
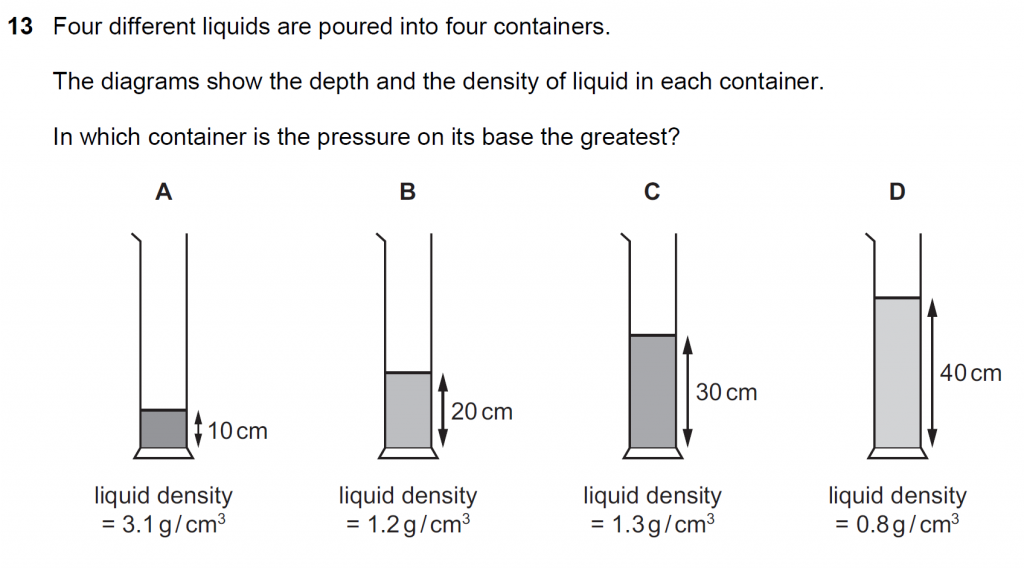
Answer : C
Solution
Pressure on the base = ρ g h, ρ = density of the liquid, and h is the depth, and g = 1000 cm/ s2, acceleration due to gravity.
A: P = ρ g h = 3.1 x 1000 x 10 = 31000
B: P = 1.2 x 1000 x 20 = 24000
C: P = 1.3 x 1000 x 30 = 39000
D: P = 0.8 x 1000 x 40 = 32000
Greatest pressure in C

Answer : A
Solution
The random collisions with air molecules of smoke particles in random directions causes random fluctuations in unbalanced net forces on the smoke particles causing it to move randomly.
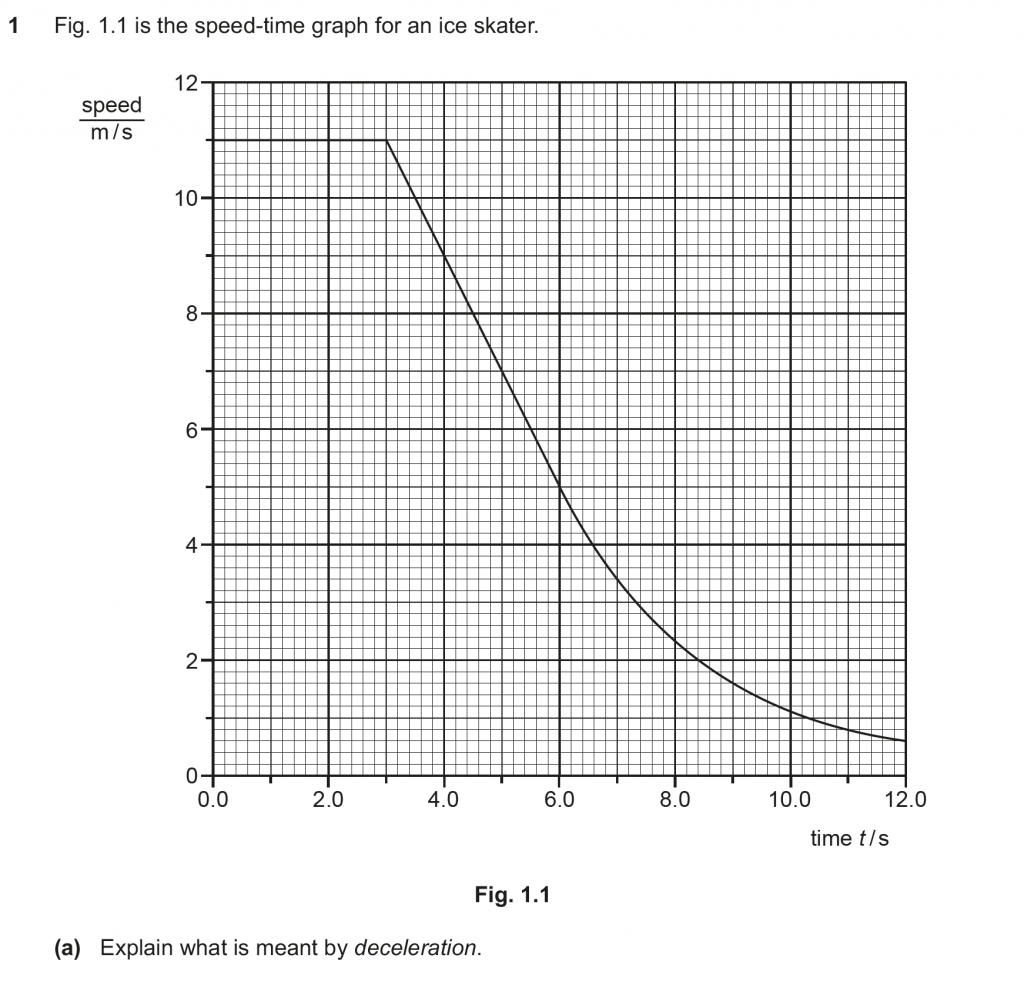
Deceleration = Rate of decrease of speed of a body with respect to time.

Distance travelled = Area under the speed – time graph
Trapezium between 3.0 and 6.0 s whose area is (11 + 5)/ 2 x 3.0 = 24 m.
Distance = 24 m

a = (11 – 5)/ 3 = 2.0 m/ s2
Deceleration = 2.0 m/ s2

Deceleration = slope of speed time graph.
After t = 6.0 s, the gradient of speed – time graph decreases, so deceleration decreases.

Resultant force = mass x deceleration
As deceleration decreases, the resultant force decreases.

Impulse = Average resultant force on the ball x time
Impulse = 180 x 0.050 = 9 N s

Impulse = change in momentum
9 = m (20 – 0)
m = 9/ 20 = 0.45 kg

v2 = u2 + 2 a s
v = 0 m/ s
u = 20 m/ s
a = – 10 m/ s2
0 = 400 – 20 H
H = 20 m
Height to which the ball rises = 20 m

Elastic Potential energy. It is due to the ball deforming in shape from that of a sphere.

Weight of an object is the gravitational force acting on it.

W = m g = 350 x 7.5 = 2625 N = 2600 N

Net force on the balloon = Its Weight – Up thrust on it
Upward direction being positive.
F = – m g + U
U = Weight of air displaced = Volume of air displaced x density of atmosphere x g
U = Volume of balloon x density of atmosphere x g = 0.30 x 0.35 x 7.5 = 0.7875 N Upward
W = m g = 0.080 x 7.5 = 0.6 N Downward
So, the resultant force on the balloon = F = – 0.6 + 0.7875 = 0.1875 N upward
So, the balloon will accelerate upward on being released from the equipment, with an acceleration of 0.1875/ 0.080 = 2.3 m/ s2.
Prediction: The balloon will move upward with an acceleration of 2.3 m/ s2.
Explanation: This is because of a larger upward up thrust acting on it than its weight which leads to an upward resultant force, of 0.188 N.