Modes of Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
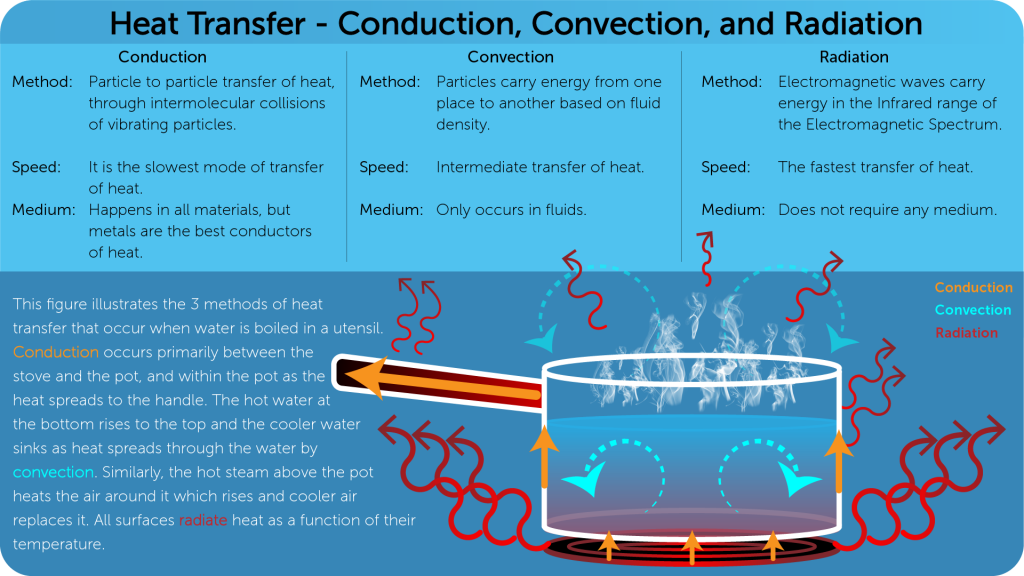
Conduction
- In this mode of transfer of heat, particle to particle transfer of heat takes place, through interatomic collisions.
- It is the slowest mode of transfer of heat.
- Metals are good conductor of heat.
- With increase in specific heat capacity, the rate of conduction of heat through the material decreases.
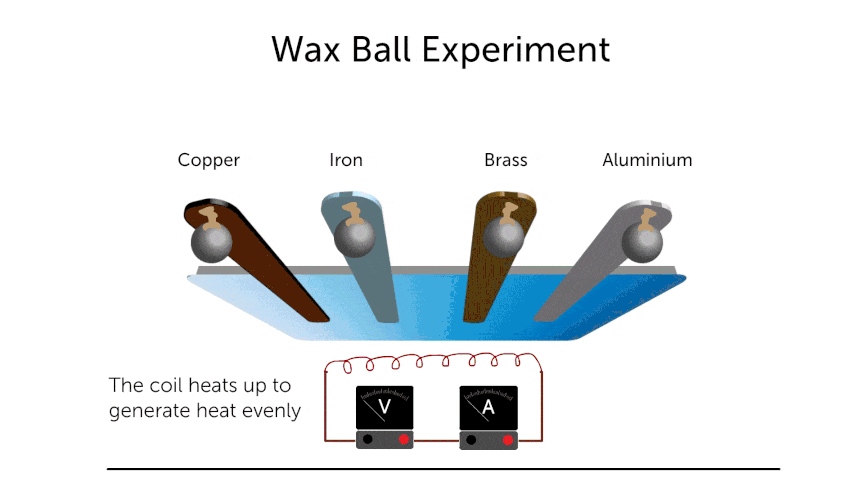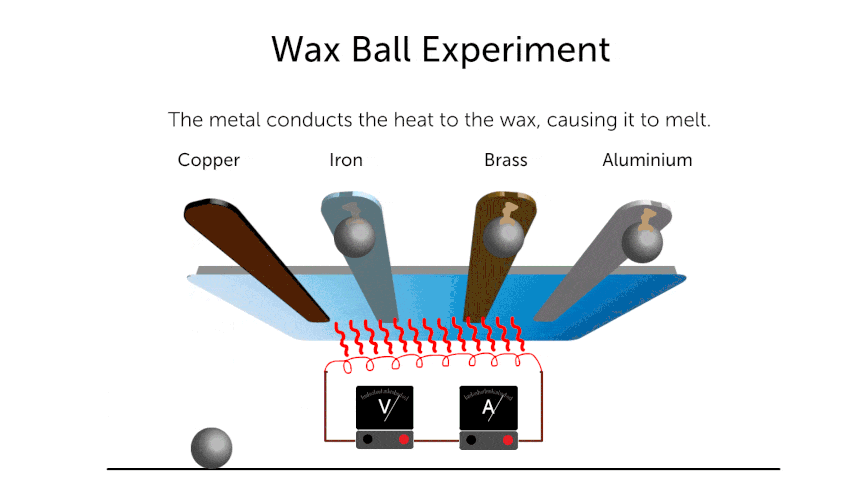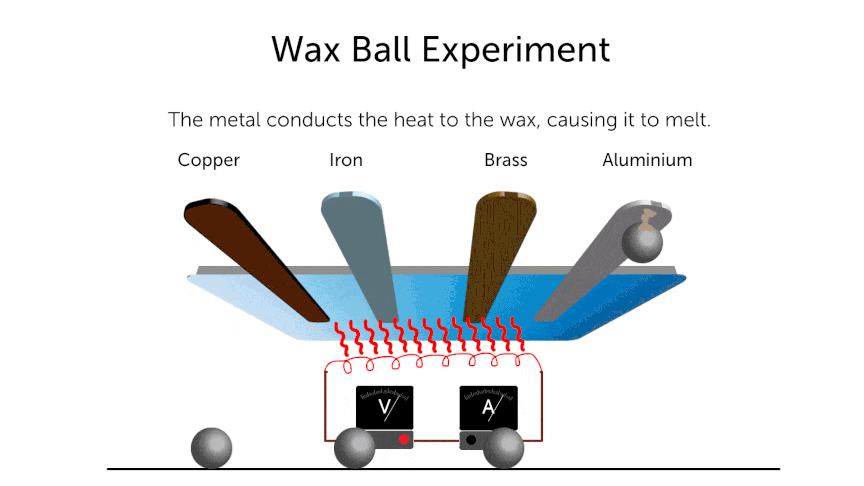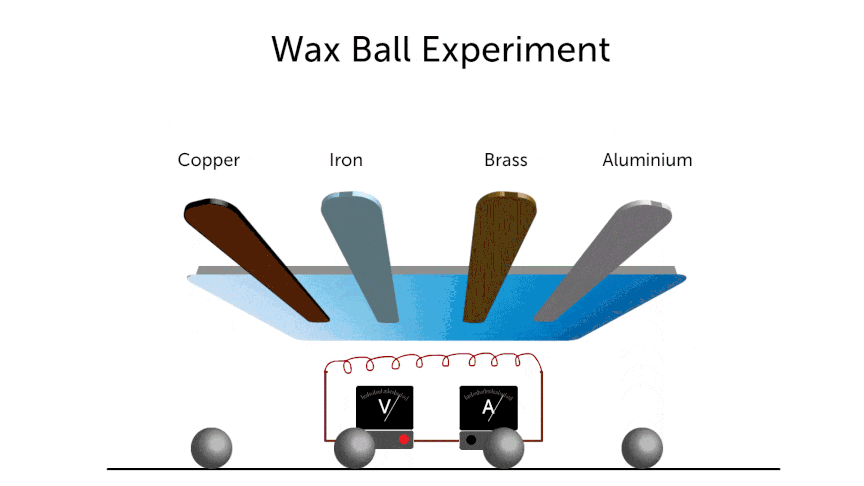
- Same amount of heat is supplied to all of the above metal rods. After time “t”
- Conduction of 1 > 2 > 3 > 4.
- For fair test —-
- Numbers of balls should be the same.
- Amount of heat supplied to each rod should be same.
- Same size of wax balls.
Convection
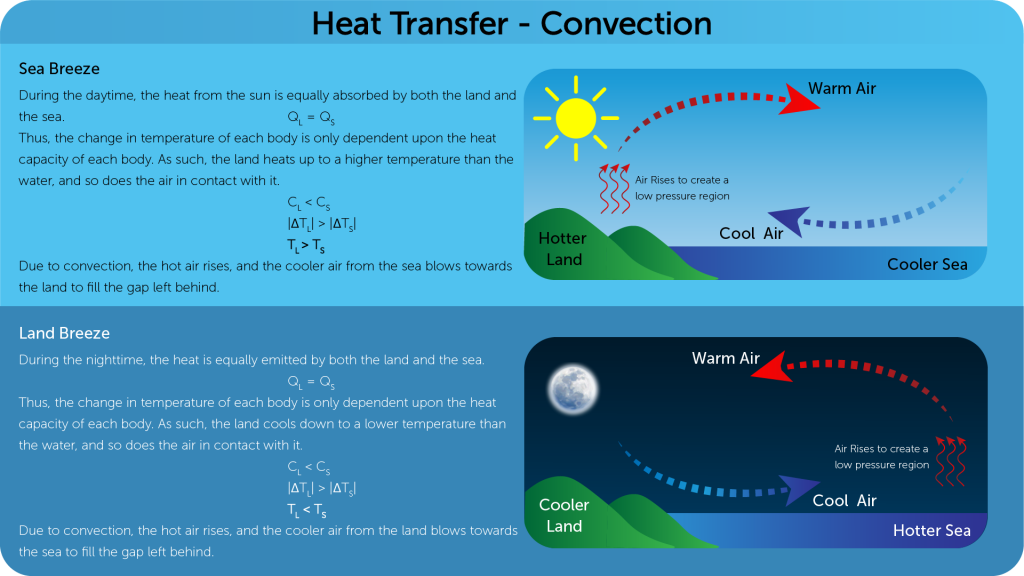
- In this process particles carry energy from one place to another.
- Convection occurs in a fluid due to density differences in the medium.
Radiation
- It is a transfer of thermal energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the infrared frequency range.
- It does not need material medium to travel.
- It is the fastest mode of transfer of heat. It travels at the speed of light in vacuum.
- The rate of absorption and emission of radiation increases with the roughness of the surface.
- Rate of emission of radiation from a dull, black surface is greater than white, shiny surface.
The reflection of radiation from a shiny, white surface is the greatest.


