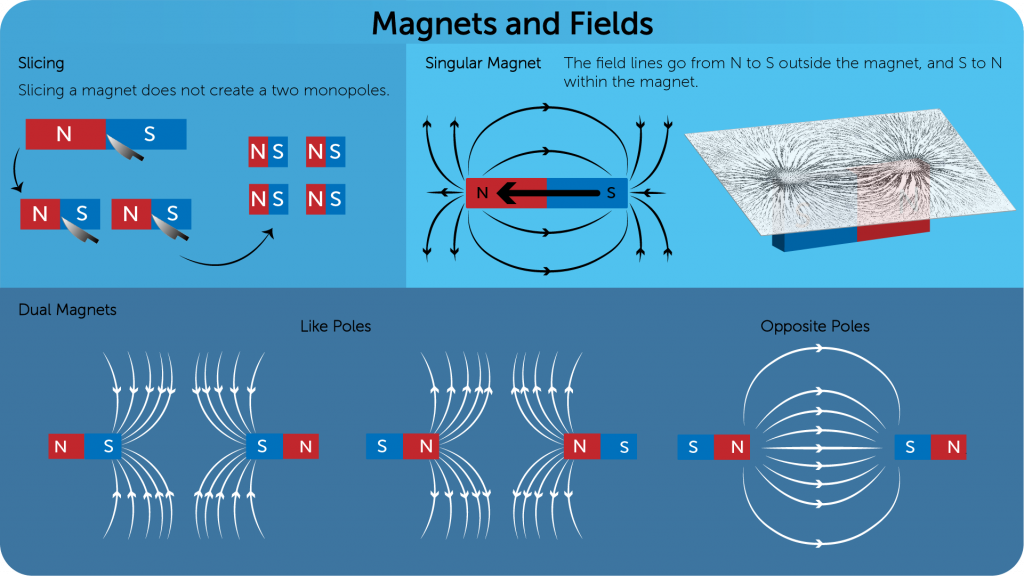
Characteristics of Magnets
- A magnet has two poles, north and south.
- A magnetic pole cannot be isolated by cutting the magnet into several parts or pieces. When you do so you create more dipole magnets, and not mono poles.
- Magnetic field line are continuous loops. Their direction is form north to south outside the magnet and south to north inside the magnet.
- A bar magnet is to be held under a piece of paper and iron filling should be sprinkled / spread on it. The iron filling will be aligned in a, pattern called magnetic fields lines.
- A magnetic compass can be used to draw the direction of magnetic field lines from north to south poles.
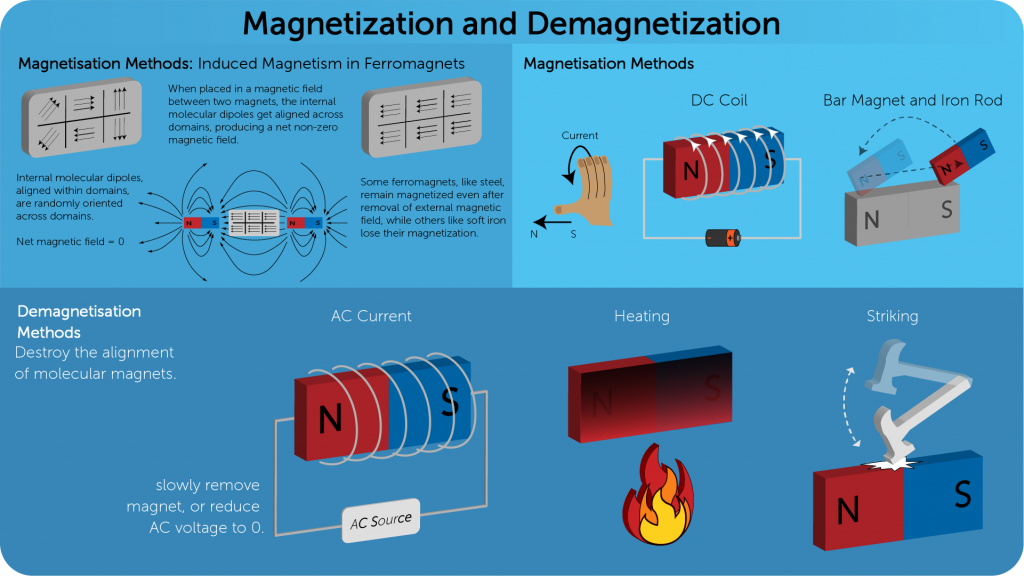
Magnetization and Demagnetization
- If a strong magnetic field is applied to the magnetic materials like soft iron, cobalt, nickel (Fe, Co, Ni), the net magnetic field will not be zero. The domains with aligned atomic magnets, align with each other and the substance gets magnetized temporarily.
- If the substance is ferromagnetic i.e. that can be magnetized easily (Steel), the domain boundaries break permanently so the substance become a permanent
- The temporary magnetization of a magnetic material can be performed by induced magnetism.
- If a Ferromagnetic substance which is not a magnet, like an iron rod is brought near a magnet, the magnet will induce an opposite polarity on the ferromagnet and then attract it. Thus, whichever end the ferromagnet is brought close to, the result is an attraction.
- Repulsion between the two objects is the sure test for both the materials to be magnets.