1.
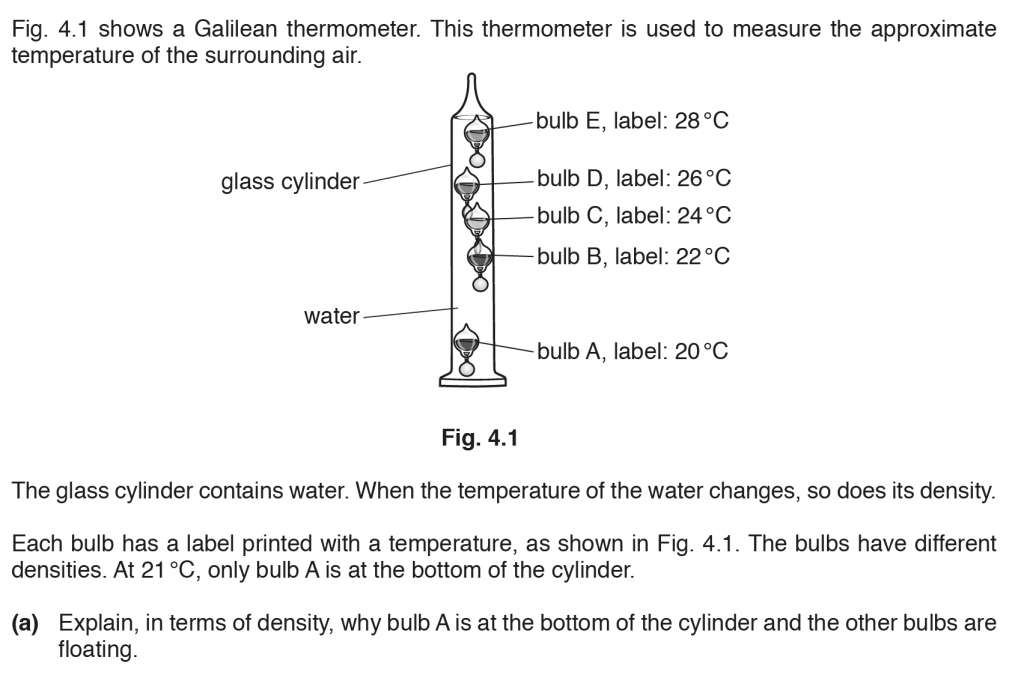
a. As temperature increases, volume increases and density decreases. If the density is lower the object will float. Bulb A is at lower temperature so lesser volume and higher density, so it at the bottom of the cylinder and others at higher temperatures and lower densities float.

b. i. The delay is because glass is a bad conductor of heat, and it takes time for water and surrounding air to reach thermal equilibrium.
b. ii. After this delay when water reaches thermal equilibrium with the air and increases to 23o C, the bulb B at 22o C would be lower in volume and therefore more dense and will therefore sink.

c. Bulb at 240C is denser than water, which is why it sinks; thus, water will have a lower limit of 24oC, and bulb D at 26oC floats, thus water will have a upper limit of 26oC.
Range, 24oC to 26oC.
2.
a. i.
a. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon.
Boiling takes place throughout the body.
b. Evaporation takes place at all temperatures.
Boiling takes place at a constant boiling point temperature.

ii. a. Condensation – Gas to Liquid.
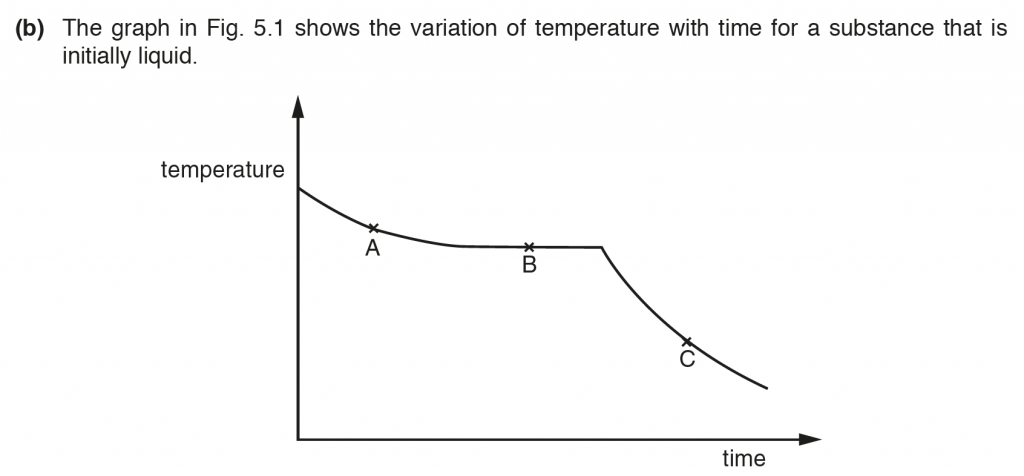

b. i.
A. Liquid cooling.
B. Liquid becoming Solid.
C. Solid cooling.

b. ii.
Liquid has a higher specific heat capacity than the solid.
3.
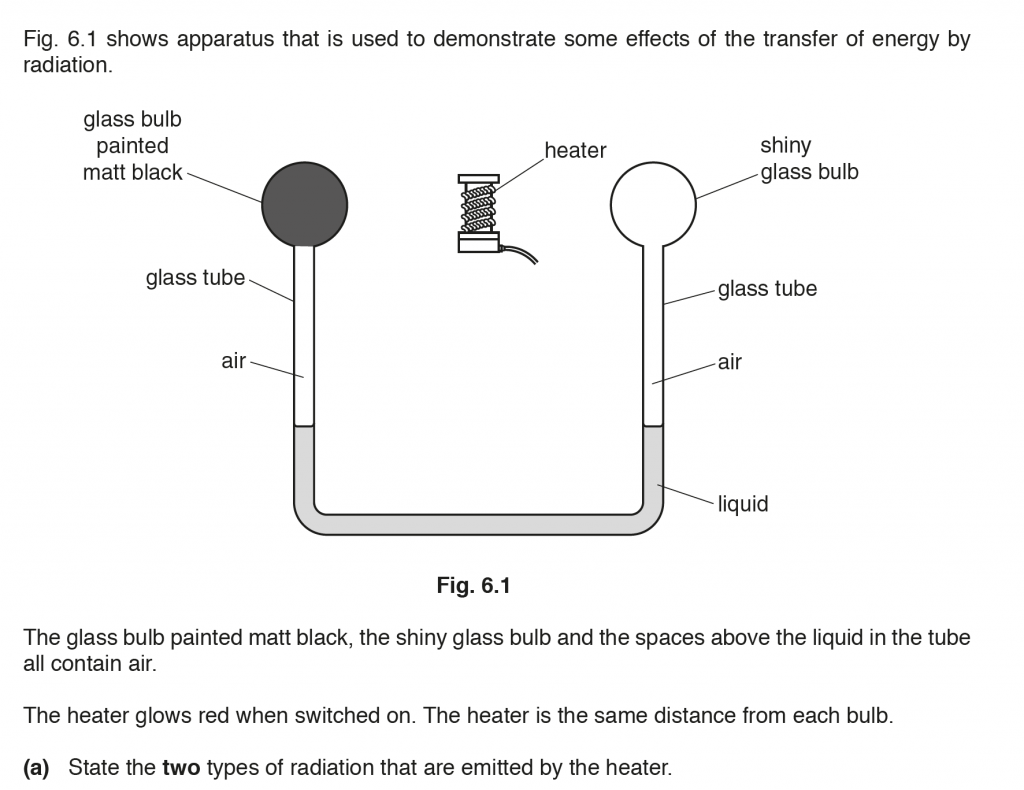
a. Visible and Infrared.

b. When the heater is switched on the glass bulb painted black absorbs more radiation than the shiny glass bulb, heating up the air column below it more, thus increasing its volume, and pushing the liquid column more. The liquid level on the left column decreases and on the right column increases.
4.

a. i. 60 joules per second.

a. ii. Radiation and either conduction or convection.
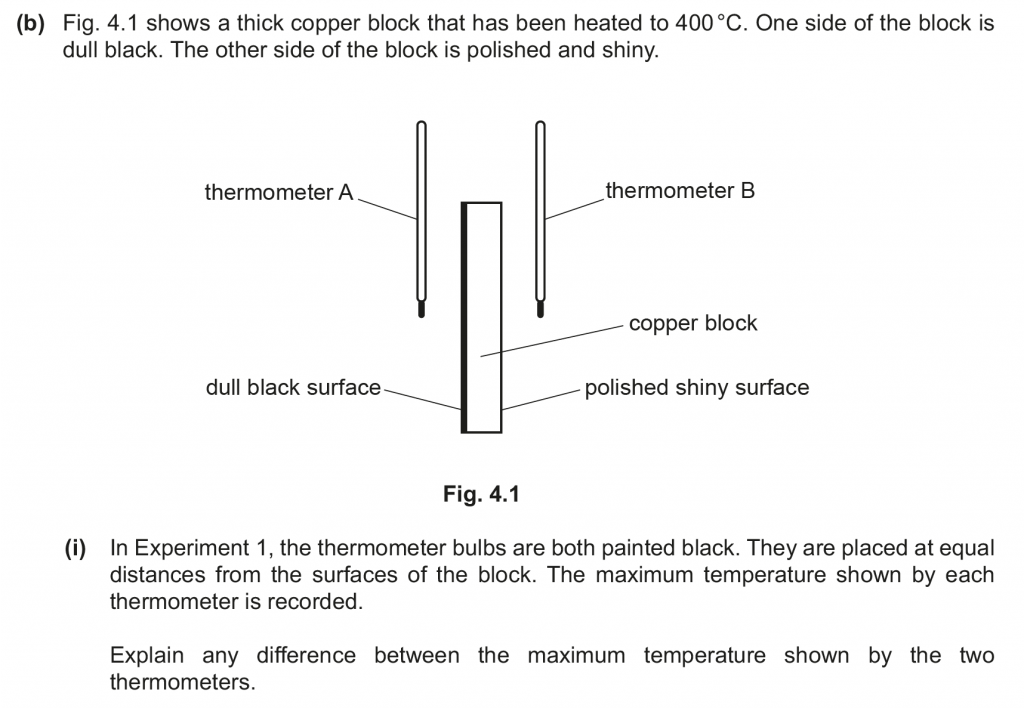
b. i. The maximum temperature shown by thermometer A is higher than that of thermometer B. This is because it is closer to the dull black surface which emits radiation at a faster rate.

b. ii. The maximum temperatures in experiment 2 would be lesser as shiny silver-coloured bulbs reflect more and absorb lesser.
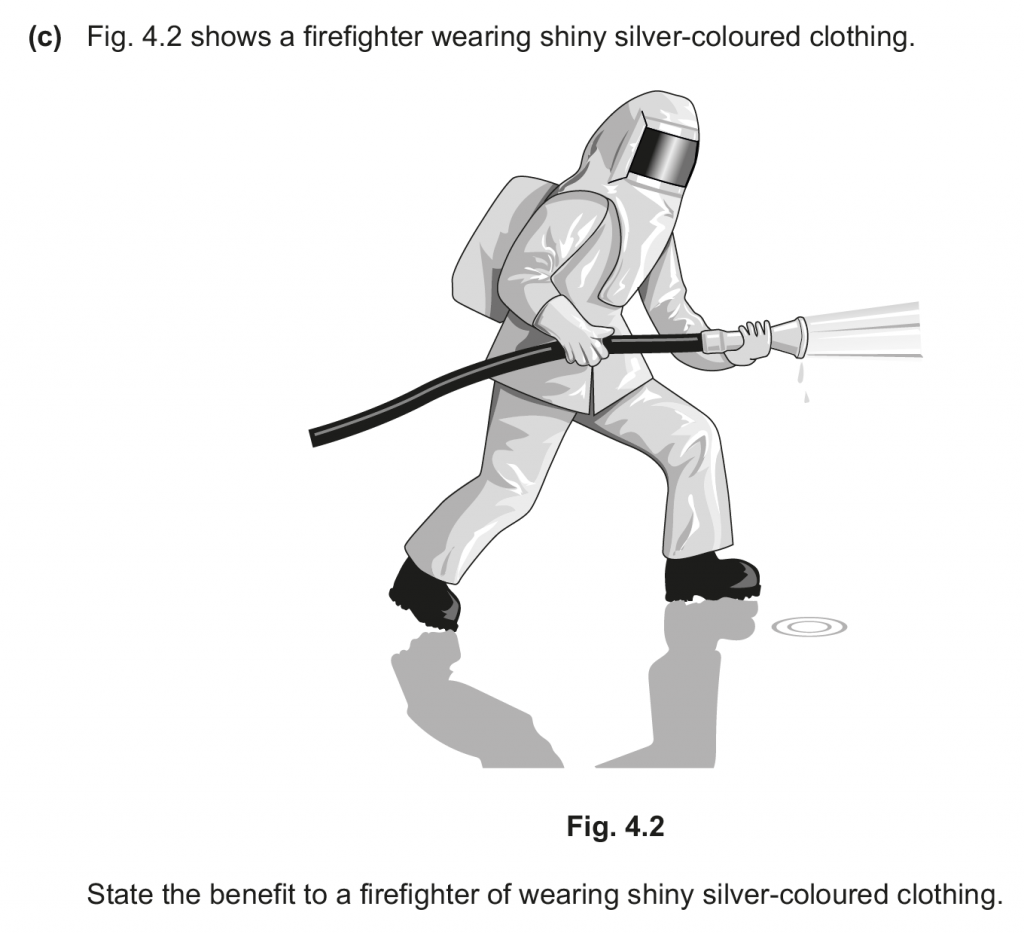
c. The shiny silver-coloured clothing will reflect more and absorb lesser, thus the firefighter would be able to tolerate higher external temperatures.
5.
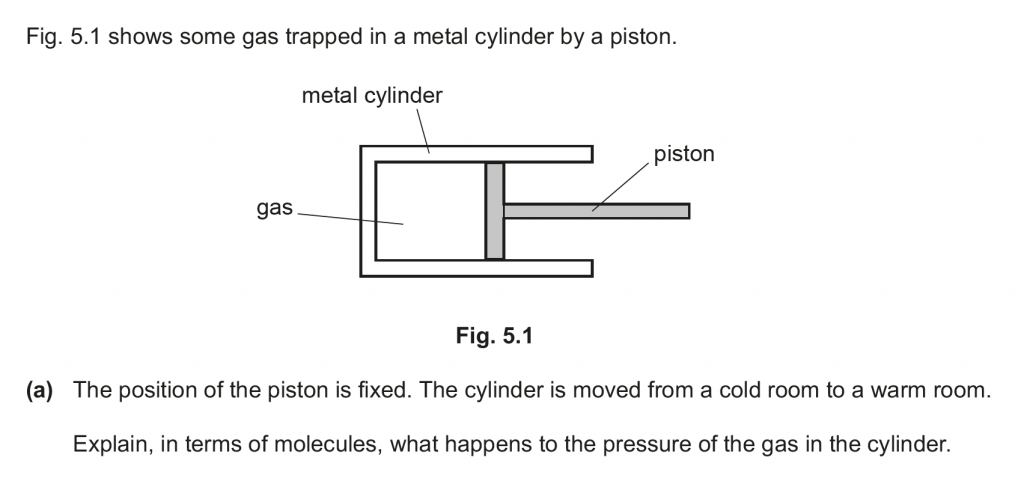
a. The molecules of gas would be at a higher average kinetic energy in the warm room, and thus would strike the walls of the cylinder at higher momenta and more frequently, thus increasing the pressure exerted.

b. Because of the pressure the gas exerts on the piston, it exerts a force on it, due to which it pushes the piston to the right, the volume increases, and thus the pressure decreases, due to which the force decreases and the piston comes to a stop.
6.

a. On colliding the momentum of the molecules changes because of the impulse exerted by the balloon on the gas molecules, and thus the gas molecules exert an impulse on the balloon, resulting in a pressure.

b. When the volume of the balloon decreases the frequency of collisions increases and the pressure increases, even though the average kinetic energy remains constant as the temperature does.

c. From Boyle’s Law
P1 V1 = P2 V2
1.1 x 105 x 500 = P2 x 200
P2 = 2.8 x 105 Pa
7.

a. i.
Q = m c ΔT
P t = 0.600 x 4200 x (100 – 20)
V I t = 201600
t = 201600/ (240 x 12) = 70 s
t = 70 s

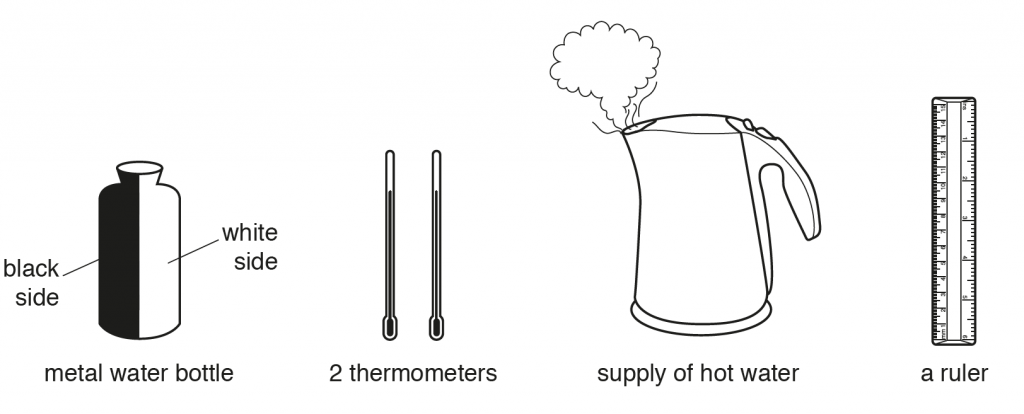
b. First put hot water in bottle and place thermometers to measure temperatures on each side of the centre of the bottle. Then place thermometers near the bottle, equidistant from the bottle, and record temperatures regularly. We expect to find the thermometer near the black side to have a higher reading or to rise faster or to have a larger temperature difference.
8.
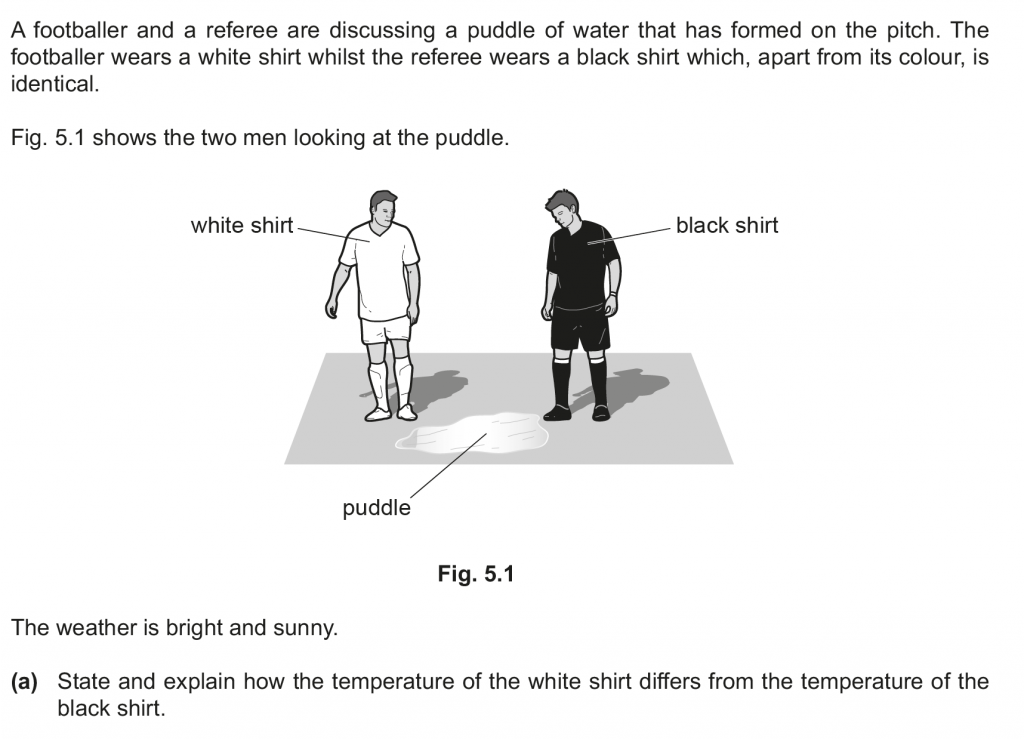
a. White shirt is a poor absorber than black coloured shirt, so it heats up lesser. The temperature of the white shirt is thus lesser than that of the black shirt.
 ‘
‘
b. i.
Change 1: Surrounding temperature Higher
Increased evaporation.
Change 2 : Less humid environment.
Increased evaporation.

b. ii. The more energetic of the water molecules leave the surface as the puddle dries, thereby taking some heat from the surface cooling it down.
9.

a. By repeated collisions, the helium particles exert an impulse on the balloon surface, and therefore a pressure.

b. i. P1 V1 = P2 V2
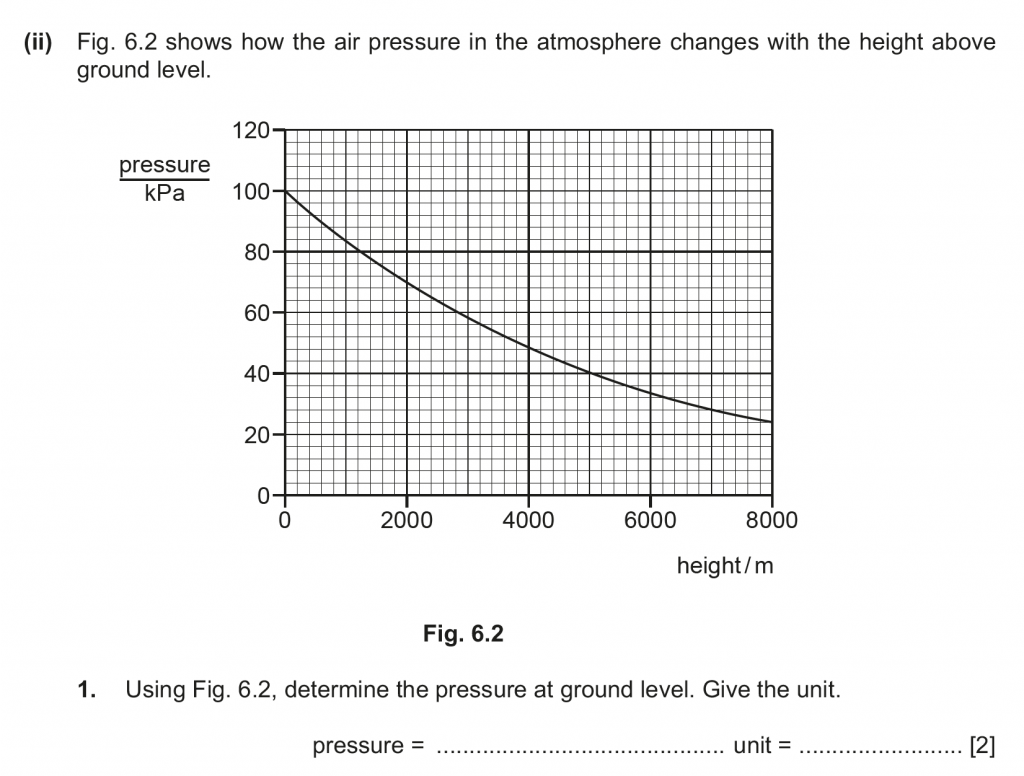
b. ii.
1. The graph shows the Pressure with height above ground.
At the ground level, for a height of 0 m above ground, the pressure is 100 kPa.

b. ii.
2. For volume to be twice the pressure must be half. Which will be at h = 3800 m.
10.
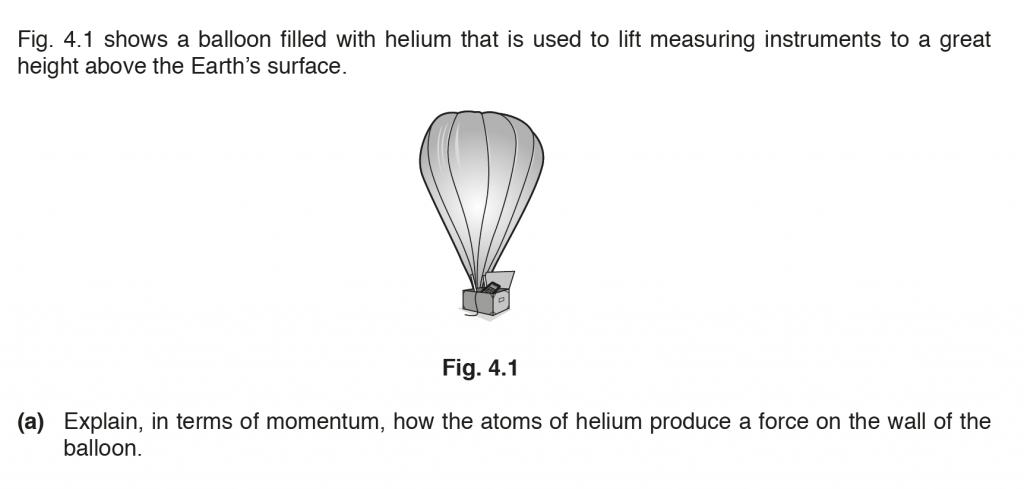
a. The helium atoms on collisions with the balloon walls undergo a change in momentum and therefore a force, to which they react to apply a force on the balloon.

b. i. The pressure is smaller at a height above the ground level, because, the volume occupied by the helium increases, so the frequency of collisions decreases.
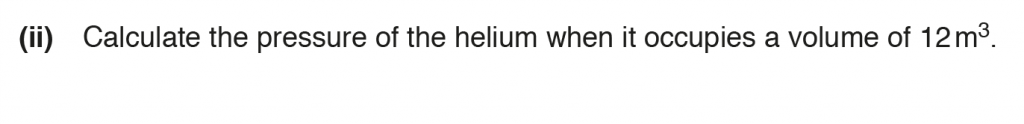
b. ii.
P1 V1 = P2 V2
1.0 x 105 x 9.6 = P2 x 12
P2 = 8.0 x 104 Pa
11.
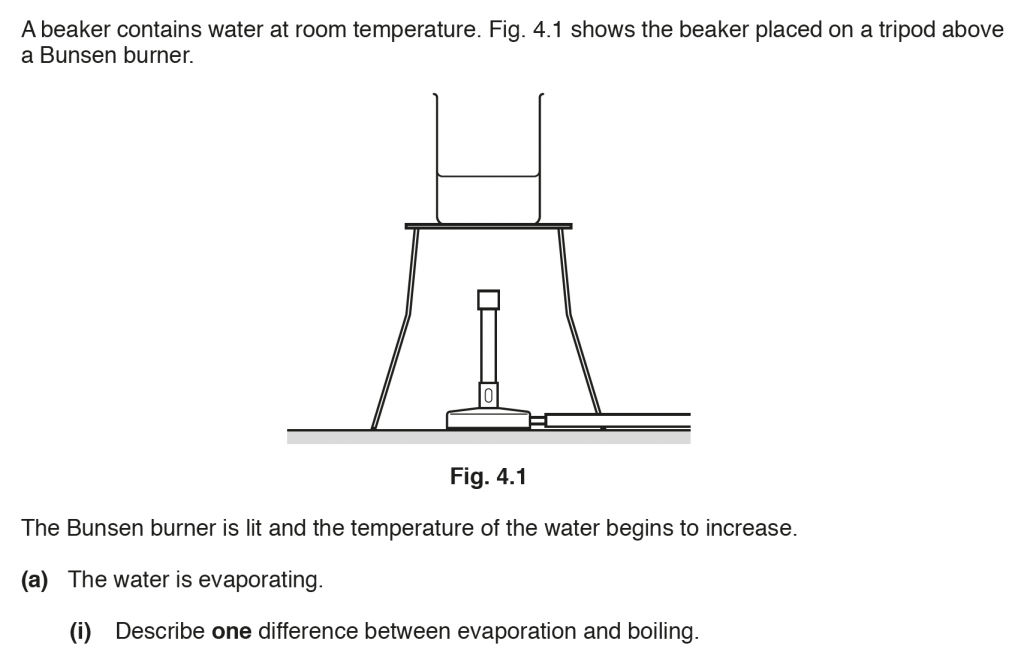
a. i. Evaporation takes place at all temperatures, boiling takes place a one particular constant temperature called the boiling point.

a. ii. As the temperature increases the rate of evaporation of the water increases. This is because at higher temperatures the average kinetic energy increases, and therefore there will be more molecules at higher energies so more molecules will leave or evaporate.

b. i. As the water reaches its boiling point it will continue to boil away at the same boiling point temperature.

b. ii.
Q = m L
P t = m L
P = m L/ t = 0.095 x 2.3 x 106/ (12 x 60) = 303 W
P = 3.0 x 102 J/s. Average rate at which energy is supplied.
12.

a. The houses in hot countries are often painted white so they reflect most of the thermal energy incident on it, and absorb less of it and thus not get heated up too much.

b. The rate of emission decrease with a drop in temperature.
13.
a. The intermolecular forces in a solid are stronger than that in a liquid.
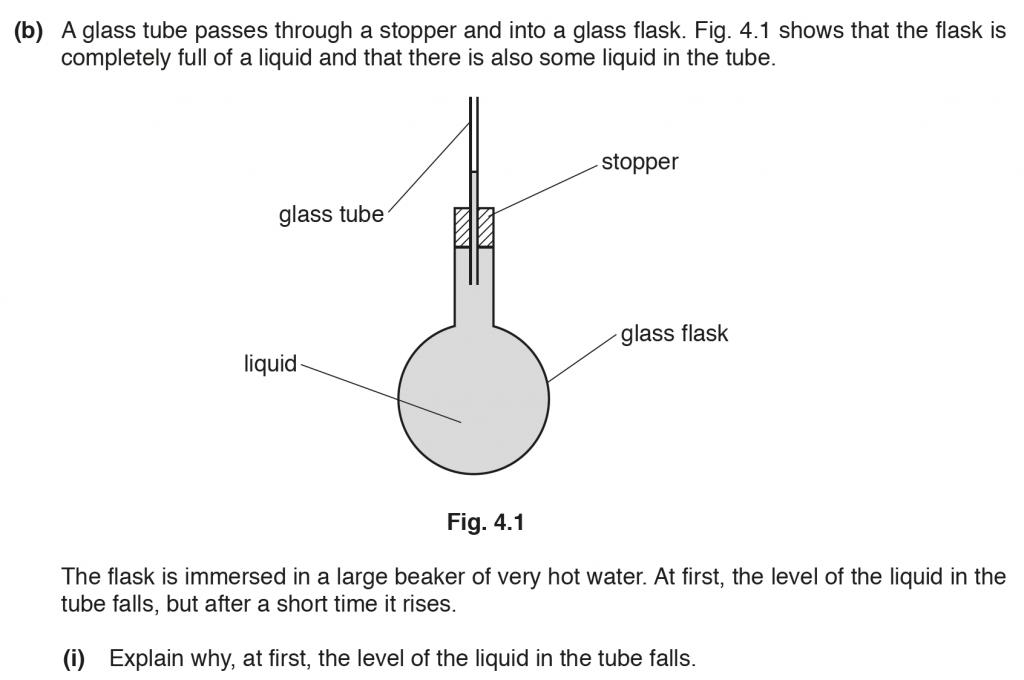
b. i. This is because the glass expands more than the liquid for the same temperature rise. The glass is a poor conductor of heat thus the liquid takes time to heat up and expand. Thus, the level of liquid in the tube drops.

b. ii. After the liquid begins to heat up and expand, its level in the glass tube rises.
14.

a. Thermal capacity of an object is the heat required by it to change in temperature bu a unit kelvin.

b. i.
Q = m c ΔT = 7.2 x (100 – 22)
Q = 562 J

b. ii. Internal energy of an object is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy of all the atoms making up the object.